Companies in every sector must comply with standards and regulations, and one of the best ways to do this is to utilize encryption. Encryption takes data that can be clearly read, also known as plaintext, and runs it through an encryption algorithm, such as symmetric key encryption or asymmetric encryption, depending on the security needs. An encryption algorithm uses a key and mathematics to convert the plaintext into ciphertext, which is an undecipherable collection of letters and symbols. The process of encryption can be reversed using the same key or the other key in a key pair, which is in a process called decryption. There are two different types of encryption: asymmetric and symmetric encryption, commonly referred to as asymmetrical vs symmetrical models. A most common question is: “Does the Caesar cipher use the symmetric encryption model?” Well, the Caesar cipher is a symmetrical encryption method based on substitution.
What’s the Difference between Asymmetrical and Symmetrical Models?
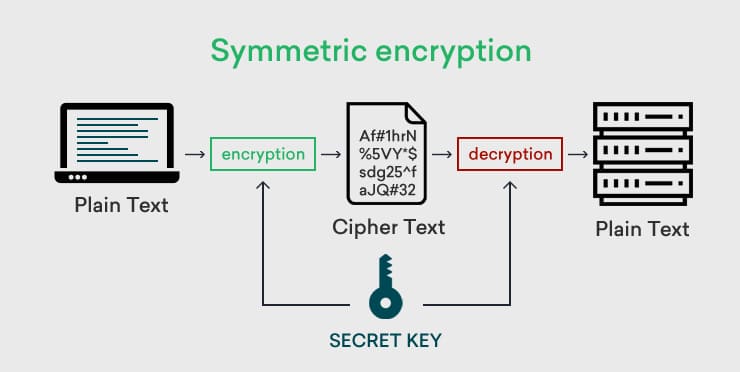
Symmetric encryption involves the use of one key for both encryption and decryption. The plaintext is read into an encryption algorithm along with a key. The key works with the algorithm to turn the plaintext into ciphertext, thus encrypting the original sensitive data. This works well for data that is being stored and needs to be decrypted at a later date, especially when symmetric key encryption is applied. The use of just one key for both encryption and decryption, as in symmetric ciphers, reveals an issue, as the compromise of the key would lead to a compromise of any data the key has encrypted. This also does not work for data-in-motion, which is where asymmetric encryption comes in. The simplicity and speed of symmetric cryptography are not disadvantages, making it suitable for high-speed data encryption.
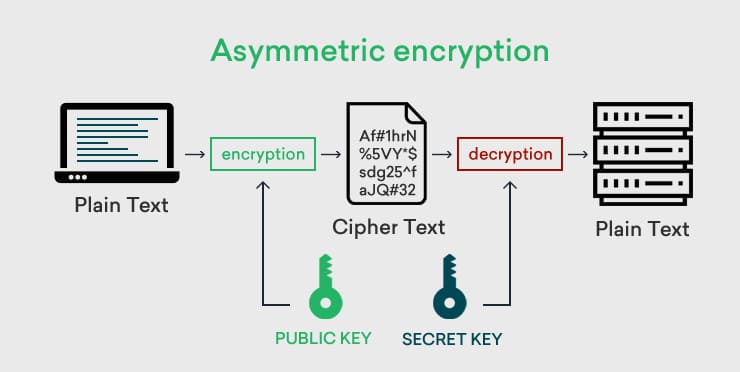
Asymmetric encryption works with a pair of keys, distinguishing it from symmetric key algorithms that use a single key. The beginning of asymmetric encryption involves the creation of a pair of keys, one of which is a public key and the other which is a private key. The public key is accessible by anyone, while the private key must be kept a secret from everyone but the creator of the key. This is because encryption occurs with the public key, while decryption occurs with the private key. The recipient of the sensitive data will provide the sender with their public key, which will be used to encrypt the data. This ensures that only the recipient can decrypt the data, with their own private key. Elliptic Curve Cryptography (ECC) is an asymmetric algorithm that is efficient in securing key exchanges and asymmetric authentication.
Uses for Asymmetric and Symmetric Encryption
Asymmetric and symmetric encryption are each better used for different situations. Symmetric encryption, with its use of a single key, is better used for data-at-rest. Data stored in databases needs to be encrypted to ensure it is not compromised or stolen. This data does not require two keys, just the one provided by symmetric encryption, as it only needs to be safe until it needs to be accessed in the future. Symmetric algorithms use two mathematically related keys. Asymmetric encryption, on the other hand, should be used on data sent in emails to other people. If only symmetric encryption were used on data in emails, the attacker could take the key used for encryption and decryption and steal or compromise the data. With asymmetric encryption, the sender and recipient ensure that only the recipient of the data can decrypt the data because their public key was used to encrypt the data. Both types of encryption are used with other processes, like digital signing or compression, to provide even more security to the data. For instance, RSA, a form of asymmetric encryption, is used in Public Key Infrastructure (PKI). Is RSA symmetric or asymmetric? RSA is classified as asymmetric encryption and is frequently used for secure data transmission. Now, another question arises: is AES encryption symmetric or asymmetric? AES is widely used for secure data encryption and is classified under symmetric encryption.
Common Asymmetric and Symmetric Encryption Algorithms
Symmetric Key Encryption examples:
- Advanced Encryption Standard (AES)
- Blowfish
- Twofish
- Rivest Cipher (RC4)
- Data Encryption Standard (DES)
Asymmetric Encryption Algorithms:
- Elliptic Curve Digital Signature Algorithm (ECDSA)
- Rivest-Shamir-Adleman (RSA)
- Diffie-Hellman
- Pretty Good Privacy (PGP)
Comparison
While asymmetric encryption is often recognized as being more advanced than symmetric encryption, organizations still use both cryptographic techniques in their security strategies. For example, symmetric encryption (RC4) is ideal for maximizing the speed of bulk data encryption or to secure communication within closed systems. On the other hand, asymmetric encryption is more beneficial for open systems where the priority is securing key exchanges, digital signatures (DSA which is an asymmetric algorithm), and authentication, particularly in cases like TLS symmetric or asymmetric models. For example, PGP and Diffie Hellman are used to encrypt emails and files and are examples of asymmetric encryption.
Here is a comparison table between symmetric and asymmetric encryption.
| Asymmetric Encryption | Symmetric Encryption | |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | A two-way function that takes in plaintext data and turns it into undecipherable ciphertext. This process utilizes a public key for encryption and a private key for decryption, which is true of asymmetric encryption models. | A two-way function that takes in plaintext data and turns it into undecipherable ciphertext. With symmetric encryption, a cipher (symmetric cipher) is known to use the same key for both encryption and decryption. |
| Use Cases |
|
|
| Advantages |
|
|
| Disadvantages |
|
|
| Common Algorithms | ECDSA, RSA, PGP | AES, Blowfish, Twofish, RC4 |

