Sign Android Package Kit (APK) files with ApkSigner using PKCS#11 library


You’re probably wondering why we would sign an APK, right? A digital signature is a method for demonstrating the authenticity of a digital file, such as a document, executable file, or, in this case, an APK, which is just a collection of files. We can practically guarantee that whoever uses an APK will receive a verifiable copy of the file they anticipated by signing the APK. Since no one else can alter this file while keeping the same signature, there are clear security benefits.
Now, to achieve this, we are integrating PKCS#11 libraries, which enables us to use enhanced security by storing keys on Hardware Security Modules (HSMs) or some kind of Key Vault. This article is going to walk you through the process of using APKSigner with our (Encryption Consulting’s) PKCS#11 Wrapper on Ubuntu and MacOS for your APK signing operations.
When it comes to APK signing operations, PKCS#11 APIs play a very important role. PKCS#11 is a very famous and widely adopted standard API that enables software to interact very smoothly with HSMs. Integrating PKCS#11 into APKSigner will allow you or your developers to sign Android APKs while ensuring that the private keys never leave a secure environment (HSMs). Your keys are protected from possible online threats in this way.
The PKCS#11 Wrapper from Encryption Consulting will give you an extra degree of dependability and trust. We guarantee outstanding performance, seamless integration, and—above all—client-side hashing. With the help of our PKCS#11 Wrapper, you can:
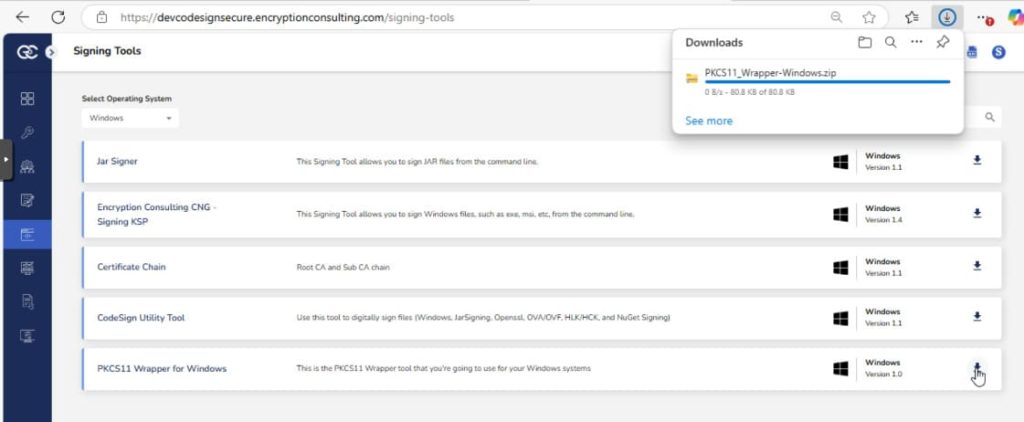
Step 1: Go to EC CodeSign Secure’s v3.01’s Signing Tools section and download the PKCS11 Wrapper for Windows.
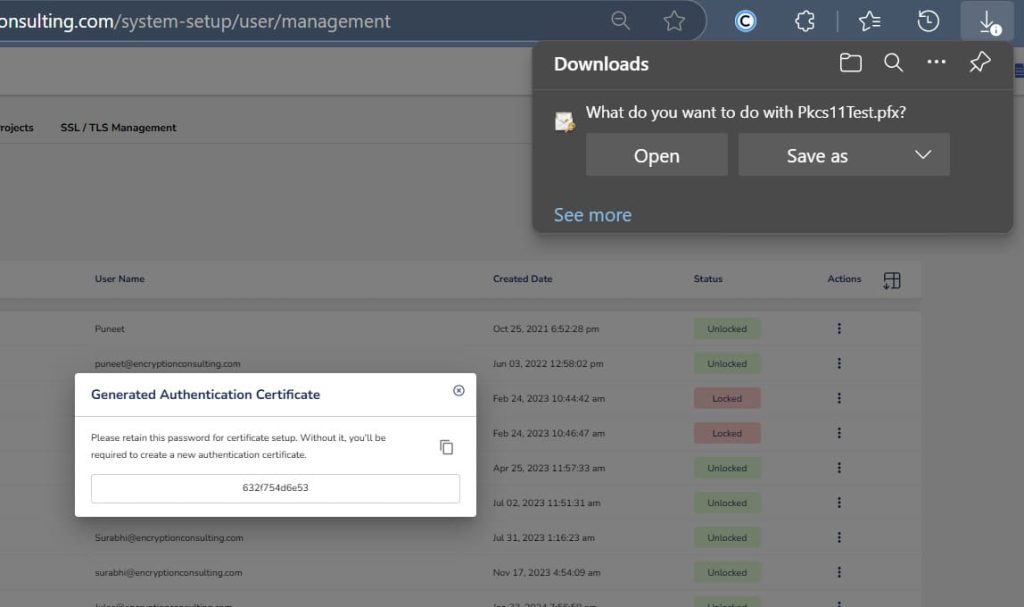
Step 2: After that, generate a P12 Authentication certificate from the System Setup > User > Generate Authentication Certificate dropdown.
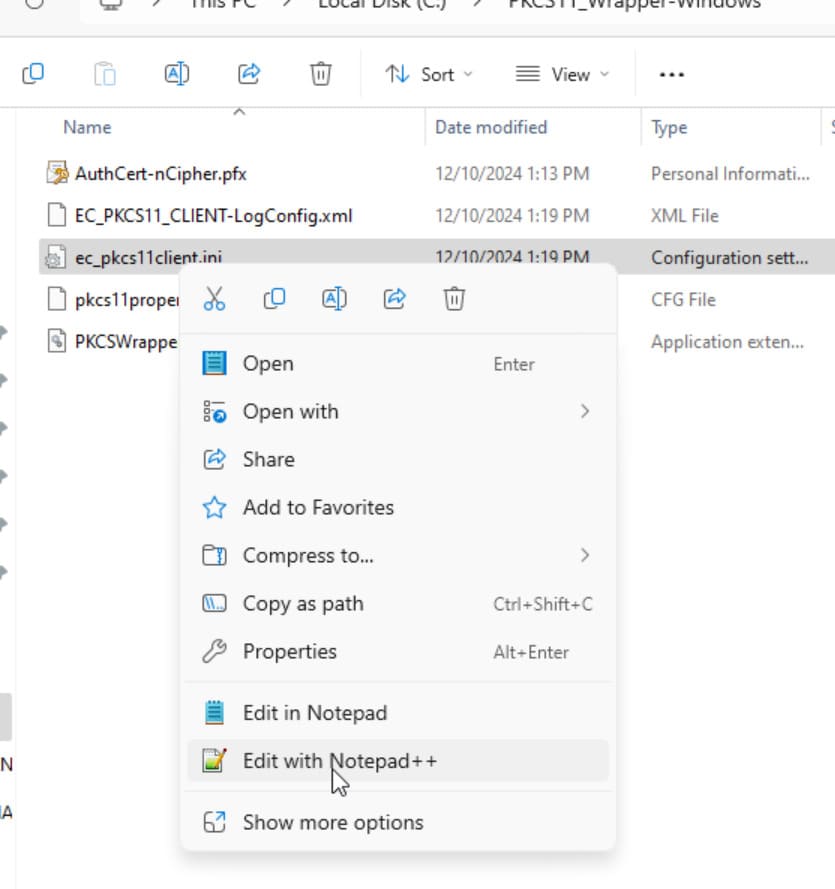
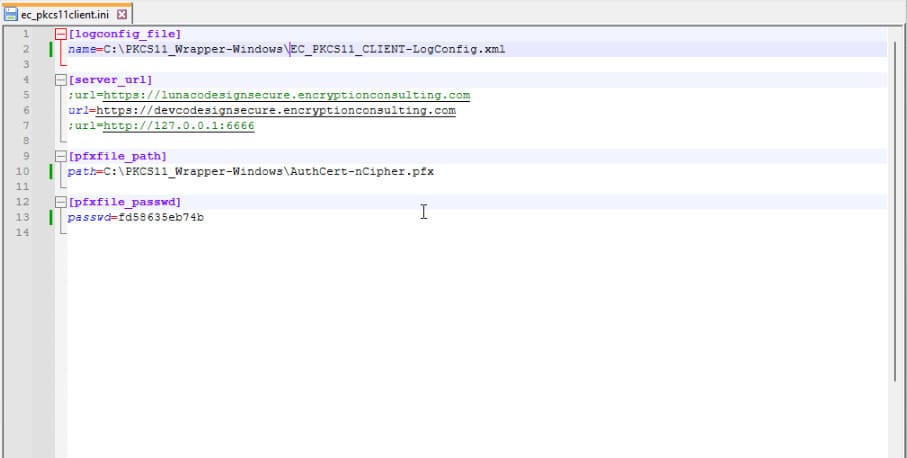
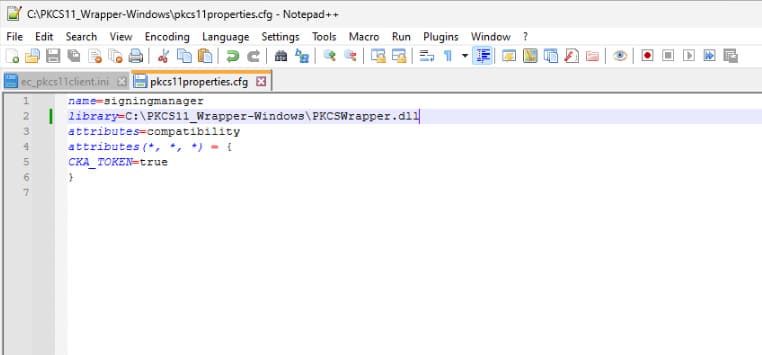
Step 3: Go to your Windows client system and edit the configuration files (ec_pkcs11client.ini and pkcs11properties.cfg) downloaded in the PKCS11 Wrapper.
Now, let’s install some prerequisites in your client system to run the PKCS11 Wrapper.
Step 1: Install Java 22 from Oracle’s official site and follow the instructions in the msi file.
Step 2: Set Java 22 as the active version by storing the bin path in the PATH variable.
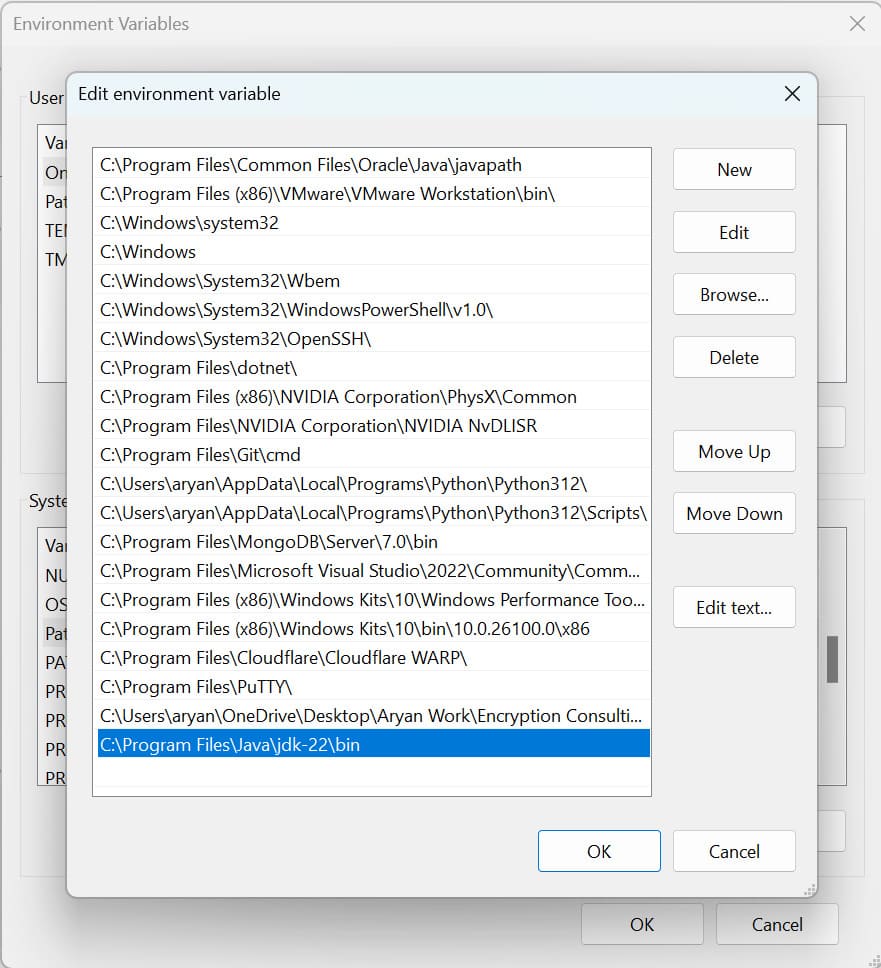
Step 3: Install the Android SDK command-line tools from this link here.
Step 4:
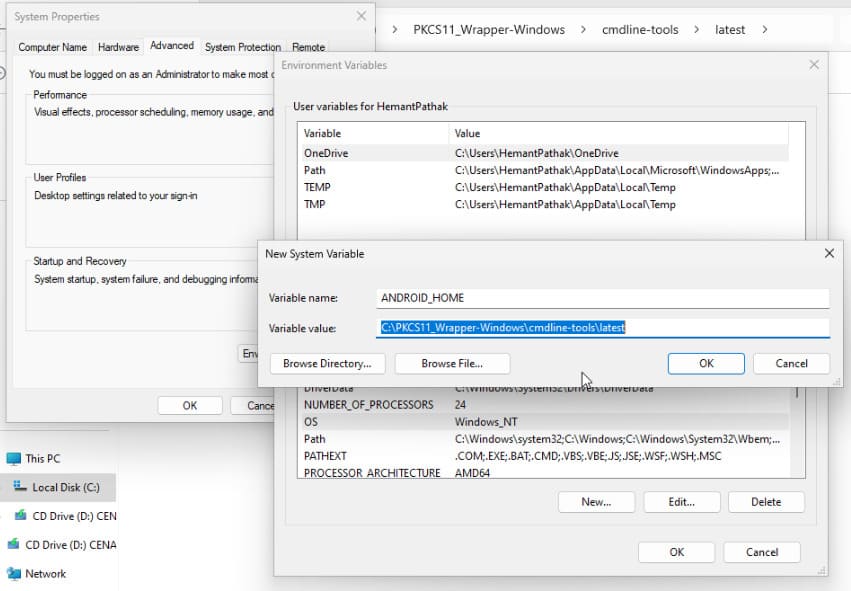
Step 5: Set an environment variable called ANDROID_HOME and set it to the path where you extracted the command line tools.
Step 6: Install Build tools using SDKManager, which contains the APKSigner: .\bin\sdkmanager –channel=0 –install “build-tools;34.0.0”
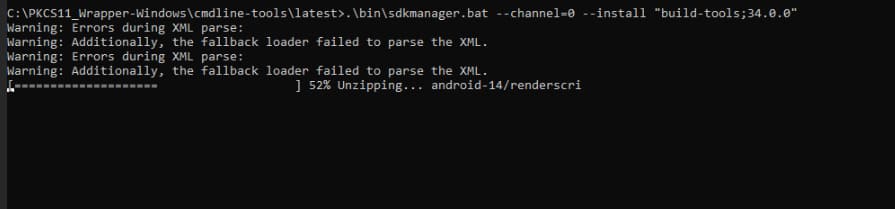
Step 7: Ensure that APKSigner is present: Apksigner.bat –version
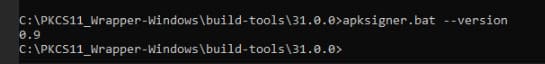
Now that all the configurations and prerequisites have been installed. Let’s perform the signing operation first.
The signing command will look something like this (ensure you run this command only inside the folder where your PKCS11 Wrapper is installed):
apksigner sign –provider-class sun.security.pkcs11.SunPKCS11 –provider-arg <path of the pkcs11properties.cfg file in your system> –ks NONE –ks-type PKCS11 –ks-pass pass:abcd1234 –ks-key-alias <private key alias> –in <path of the APK file you want to sign> –out <path of the Signed APK file>
For Example: apksigner sign –provider-class sun.security.pkcs11.SunPKCS11 –provider-arg C:\Users\riley\Downloads\PKCS11_Wrapper-Windows\pkcs11properties.cfg –ks NONE –ks-type PKCS11 –ks-pass pass:secretpassword –ks-key-alias gpg2 –in Sample.apk –out signed.apk
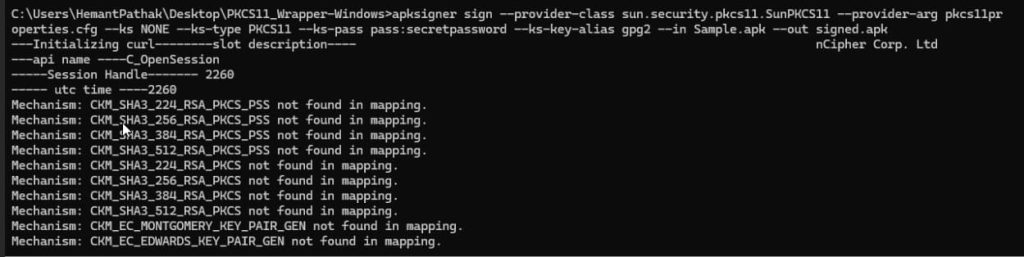
After successfully signing the APK, let’s verify it using this command:
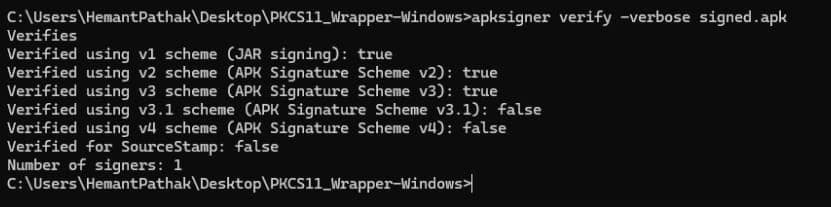
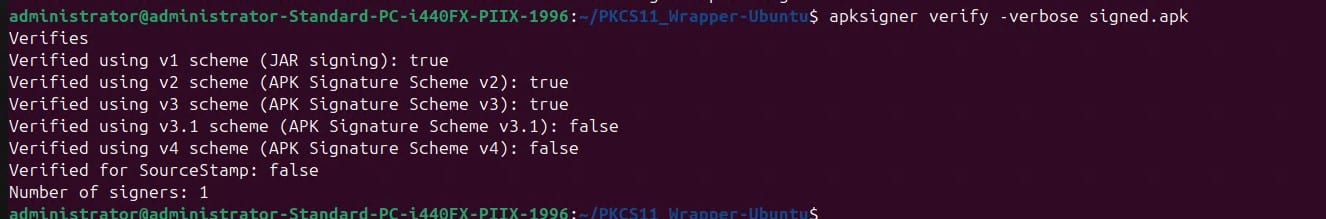
apksigner verify -verbose <path of the signed APK file>
For example: apksigner verify -verbose signed.apk
Here are the prerequisites for using our PKCS#11 Wrapper in your system. Before starting, ensure the following are ready (you can refer to the CONFIGURING PKCS#11 WRAPPER section for the steps):
Step 1: Go to EC CodeSign Secure’s v3.01’s Signing Tools section and download the PKCS#11 Wrapper for Ubuntu.
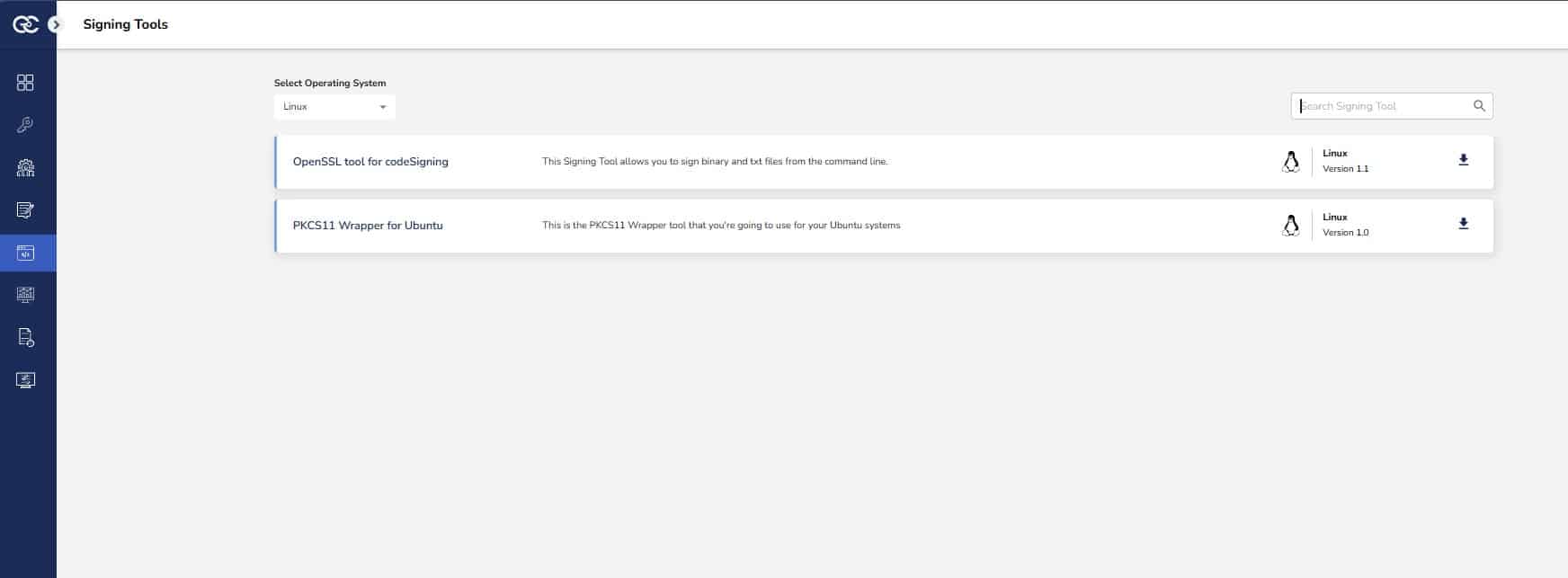
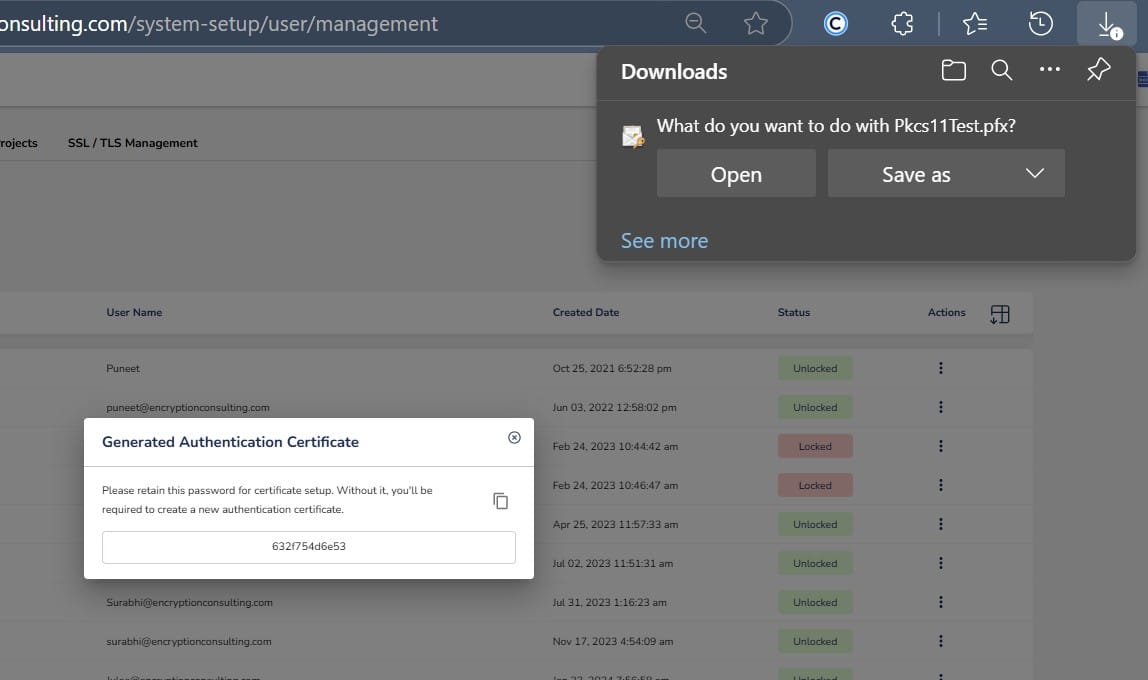
Step 2: After that, generate a P12 Authentication certificate from the System Setup > User > Generate Authentication Certificate dropdown.
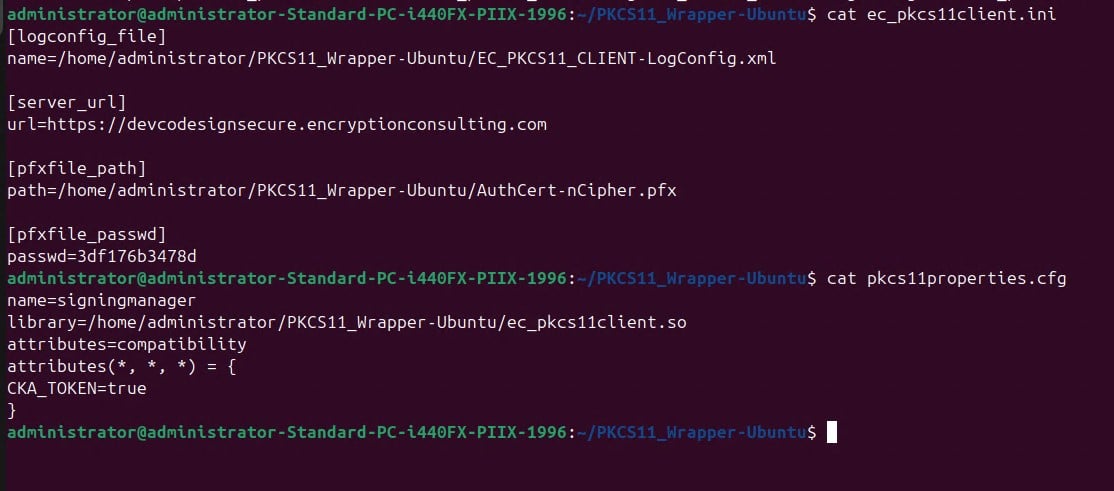
Step 3: Go to your Ubuntu client system and edit the configuration files (ec_PKCS#11client.ini and PKCS#11properties.cfg) downloaded in the PKCS#11 Wrapper.
Now, let’s configure your client system to run the PKCS#11 Wrapper.
Step 1: Install Java 8: sudo apt install openjdk-8-jdk
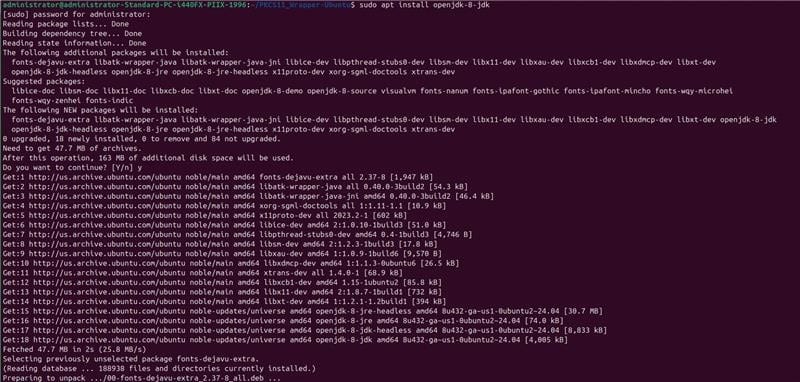
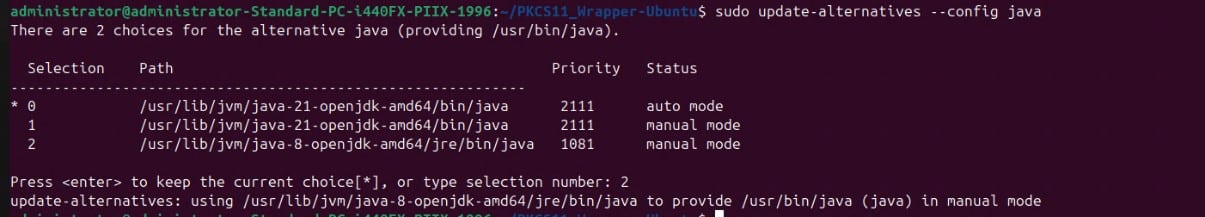
Step 2: Set Java 8 as the active version: sudo update-alternatives –config java
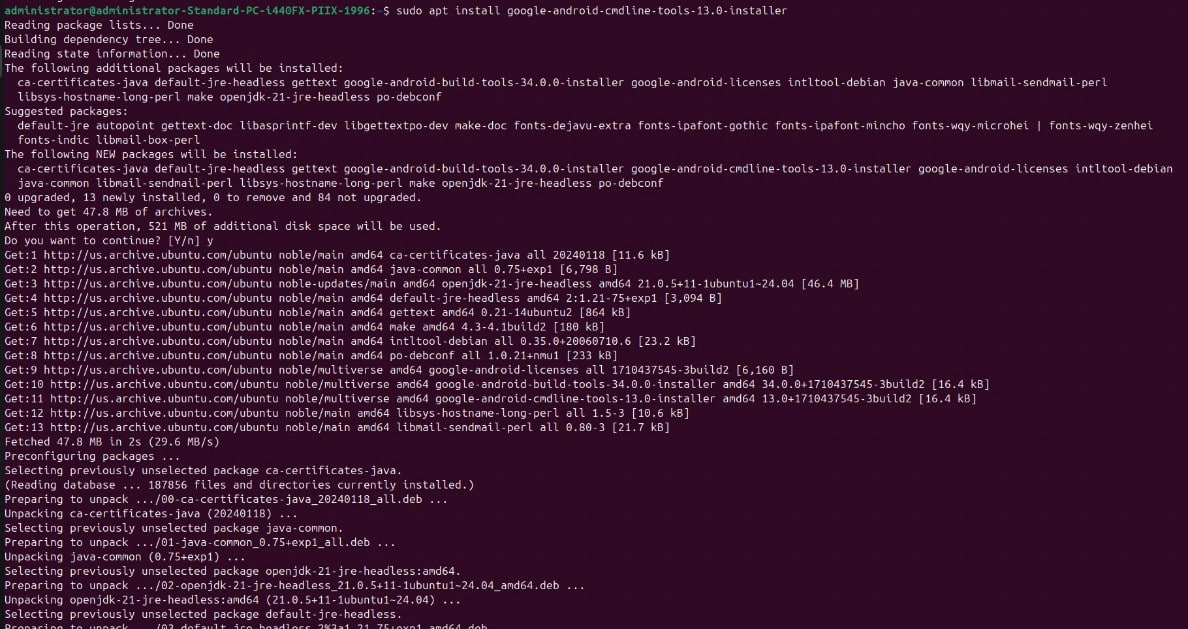
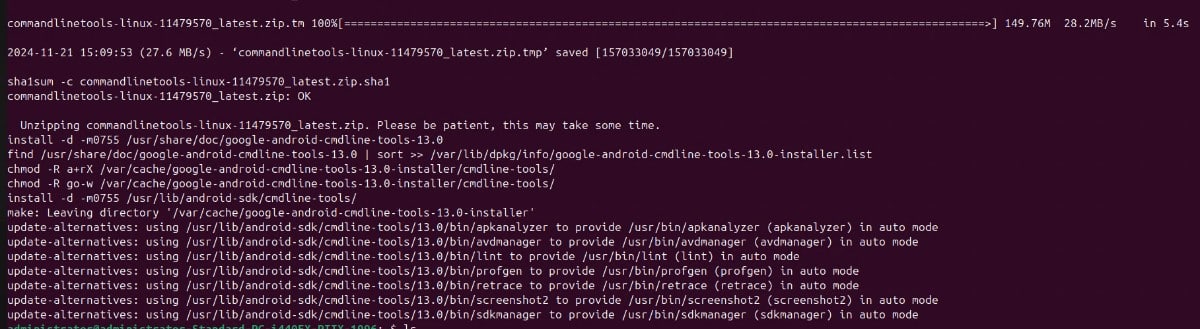
Step 3: Install the Android SDK command-line tools: sudo apt install google-android-cmdline-tools-13.0-installer
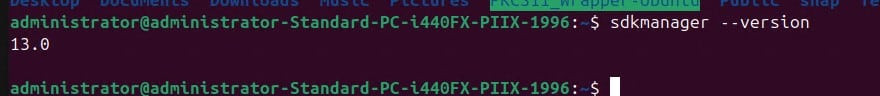
Step 4: Ensure that the SDK Manager for Android Studio has been properly installed: sdkmanager –version
Step 5: Install Build tools using SDKManager, which contains the APKSigner: sdkmanager “build-tools;34.0.0”
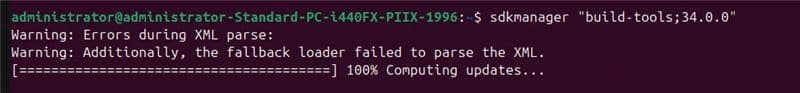
Step 6: Ensure that APKSigner is present: apksigner –version

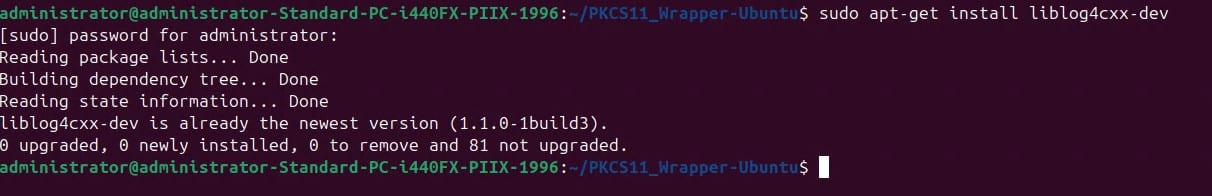
Step 7: Two packages are required to run the PKCS#11 Wrapper on your system. First, install liblog4cxx-dev using: sudo apt-get install liblog4cxx-dev
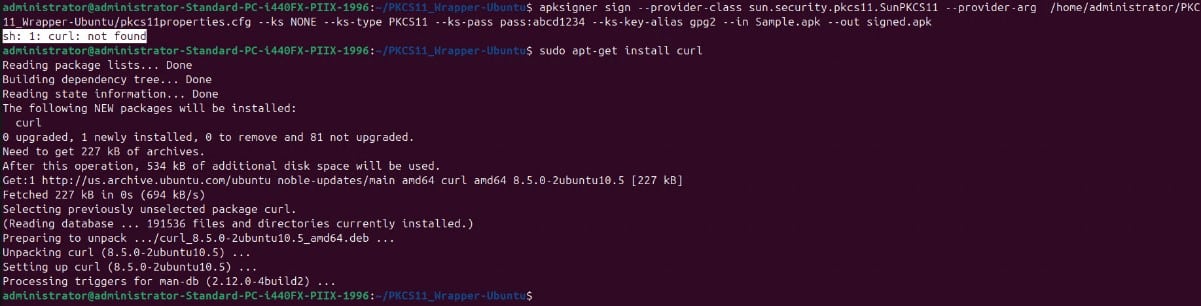
Step 8: The last prerequisite is to install the curl package: sudo apt-get install curl
Now that all the configurations and prerequisites have been installed. Let’s perform the signing operation first.
The signing command will look something like this (ensure you run this command only inside the folder where your PKCS#11 Wrapper is installed):
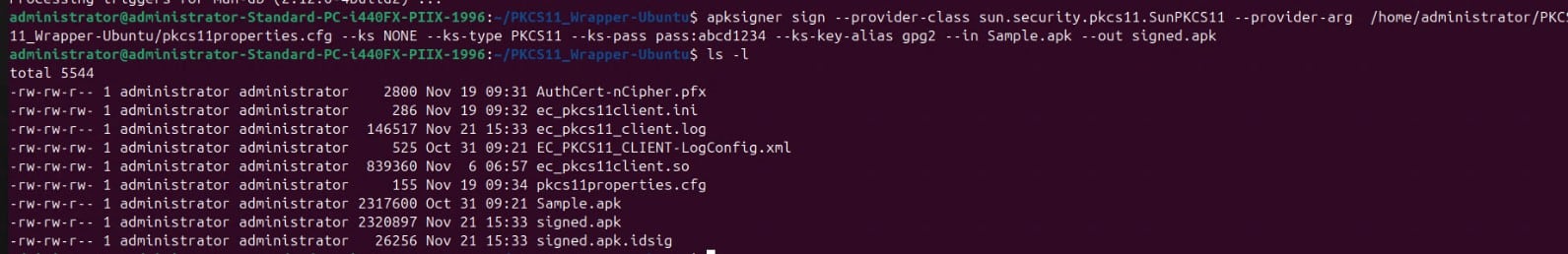
apksigner sign –provider-class sun.security.PKCS#11.SunPKCS#11 –provider-arg <path of the PKCS#11properties.cfg file in your system> –ks NONE –ks-type PKCS#11 –ks-pass pass:abcd1234 –ks-key-alias <private key alias> –in <path of the APK file you want to sign> –out <path of the Signed APK file>
For Example: apksigner sign –provider-class sun.security.PKCS#11.SunPKCS#11 –provider-arg /home/administrator/PKCS#11_Wrapper-Ubuntu/PKCS#11properties.cfg –ks NONE –ks-type PKCS#11 –ks-pass pass:abcd1234 –ks-key-alias gpg2 –in Sample.apk –out signed.apk
After successfully signing the APK, let’s verify it using this command:
apksigner verify -verbose <path of the signed APK file>
For example: apksigner verify -verbose signed.apk
Here are the prerequisites for using our PKCS#11 Wrapper in your system. Before starting, ensure the following are ready (you can refer to the CONFIGURING PKCS#11 WRAPPER section for the steps):
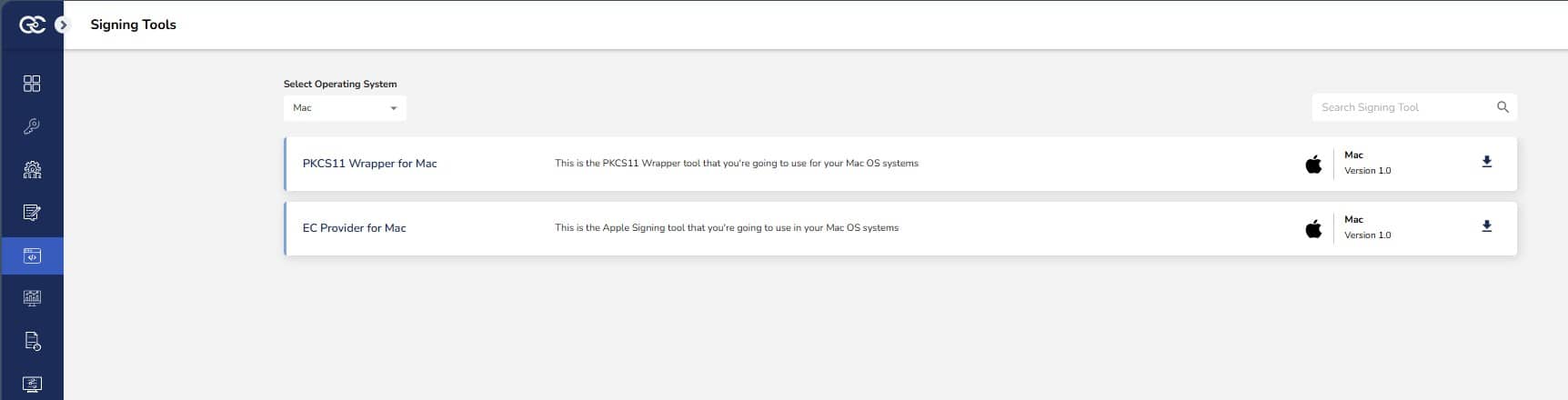
Step 1: Go to EC CodeSign Secure’s v3.01’s Signing Tools section and download the PKCS11 Wrapper for MacOS.
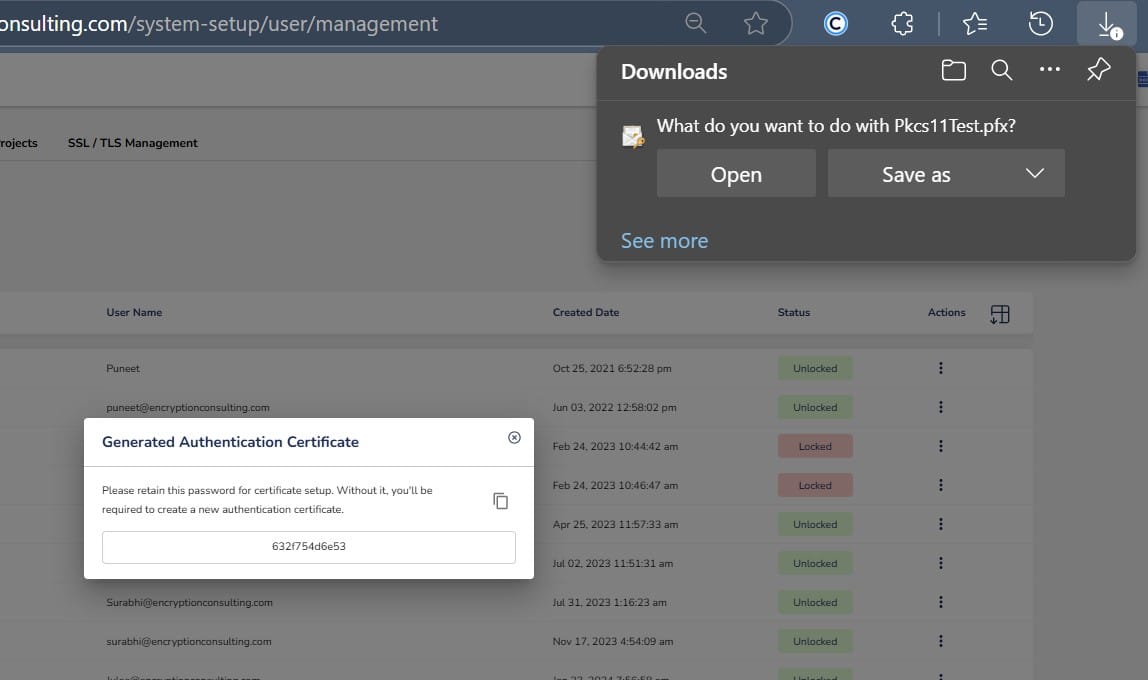
Step 2: After that, generate a P12 Authentication certificate from the System Setup > User > Generate Authentication Certificate dropdown.
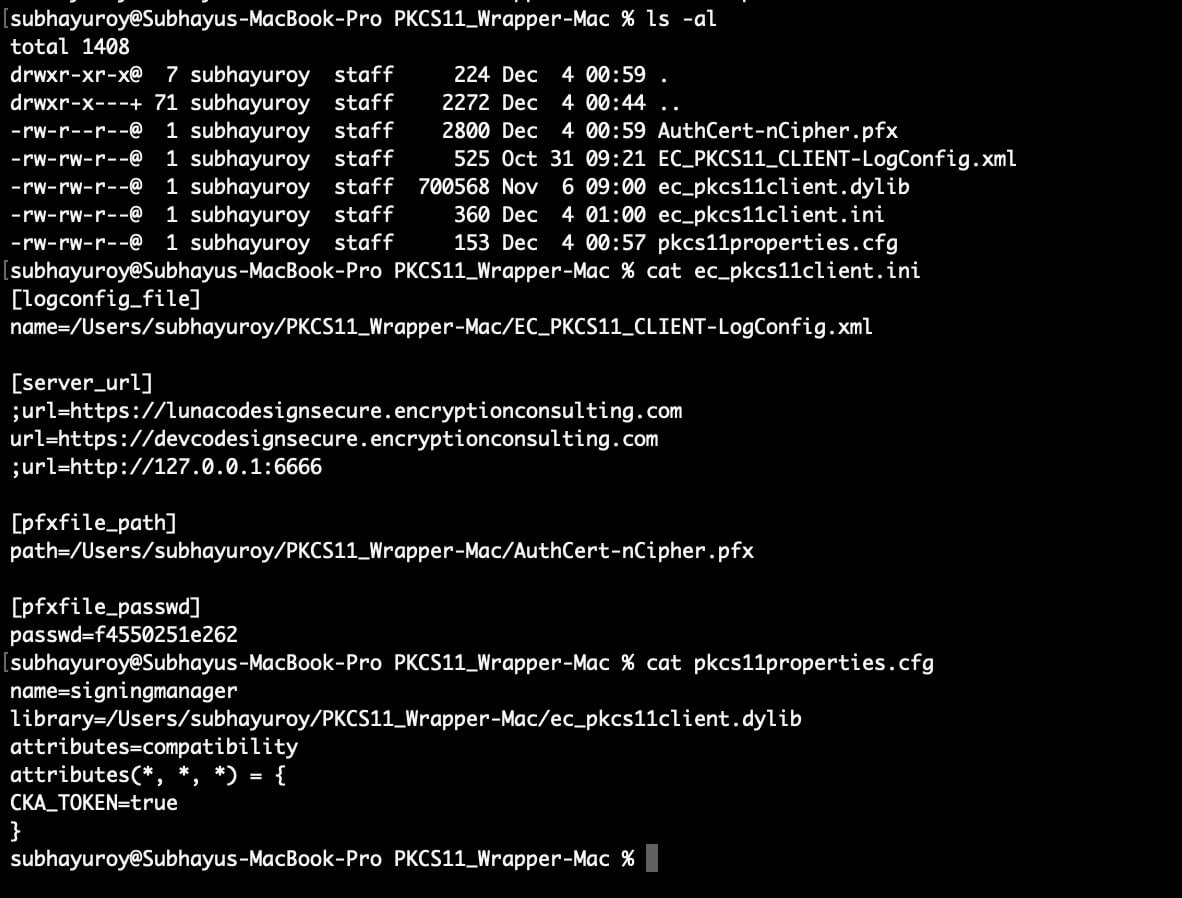
Step 3: Go to your MacOS client system and edit the configuration files (ec_pkcs11client.ini and pkcs11properties.cfg) downloaded in the PKCS11 Wrapper.
Now, let’s configure your client system to run the PKCS11 Wrapper.
Step 1: Install Java 17: brew install openjdk@17
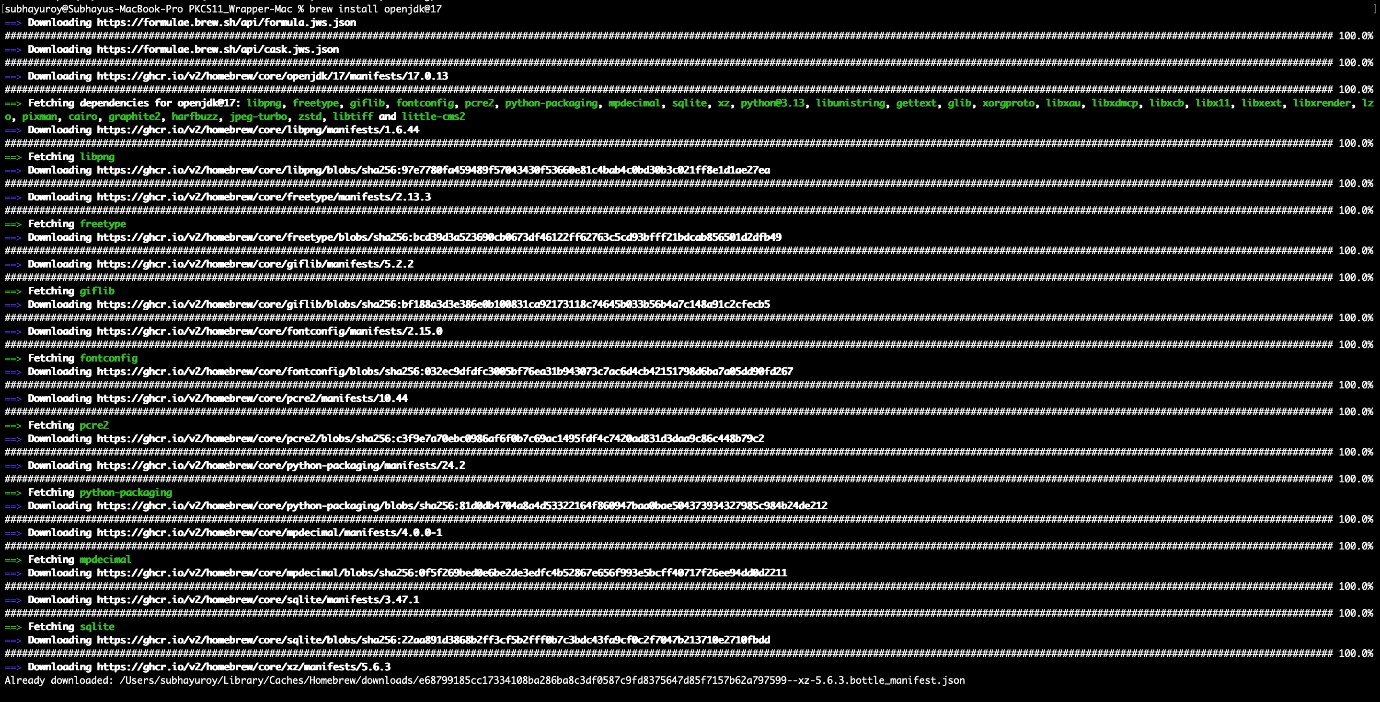
Step 2: Set Java 17 as the active version:
Add these lines: export JAVA_HOME=$(/usr/libexec/java_home -v 17)
export PATH=$JAVA_HOME/bin:$PATH
And then run: source ~/.zshrc # or ~/.bash_profile
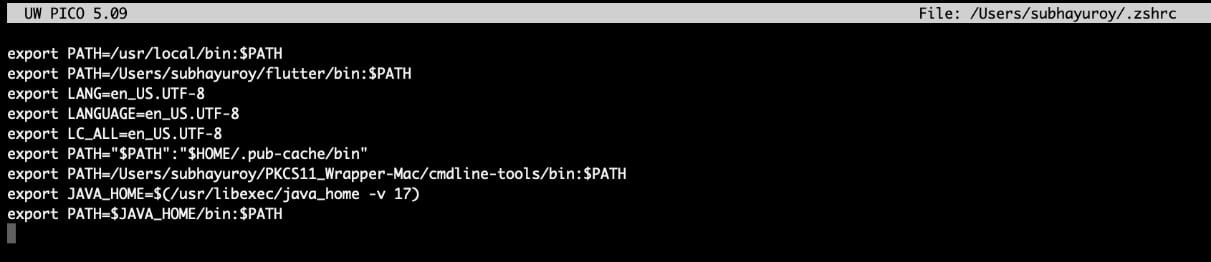
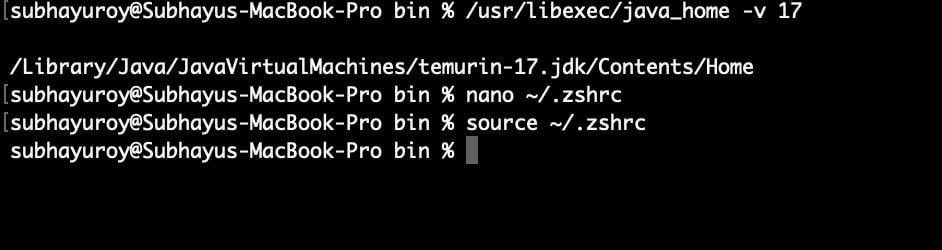
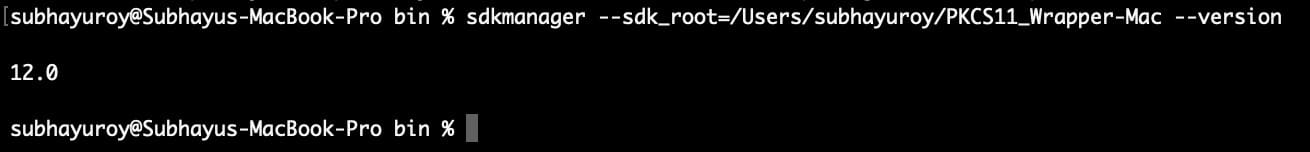
Step 3: Install the Android SDK command-line tools from this site.
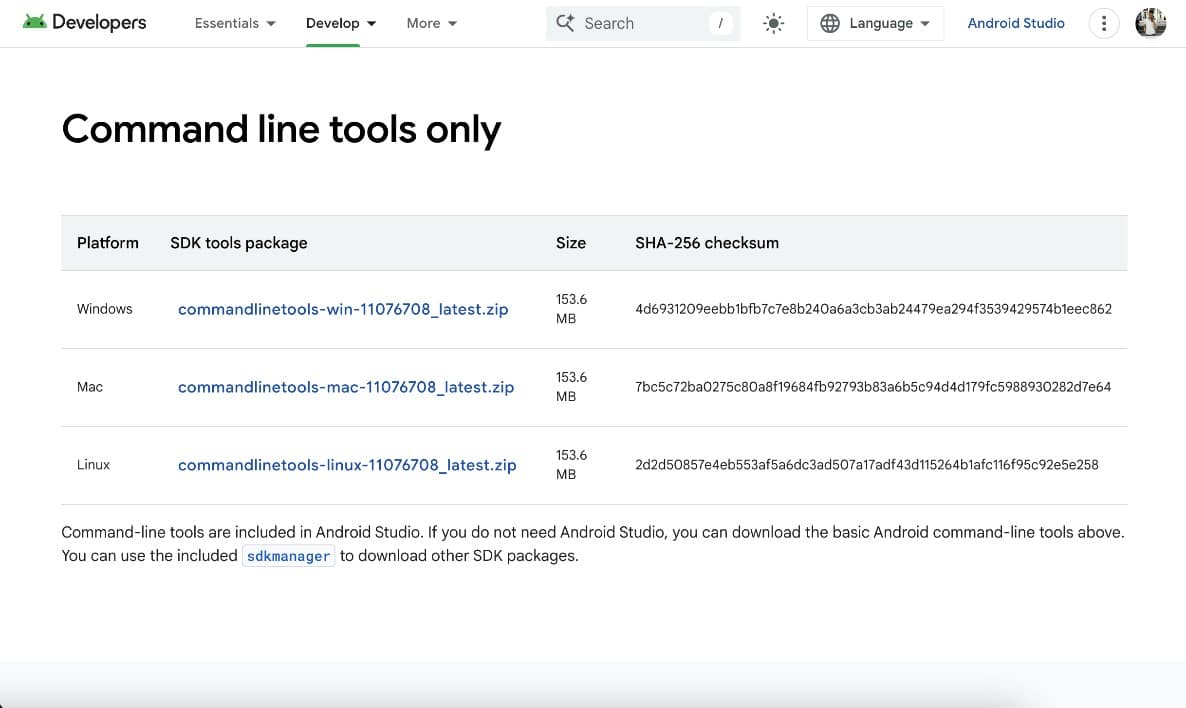
Step 4: Ensure that the SDK Manager for Android Studio has been properly installed: sdkmanager –sdk_root=/Users/subhayuroy/PKCS11_Wrapper-Mac –version
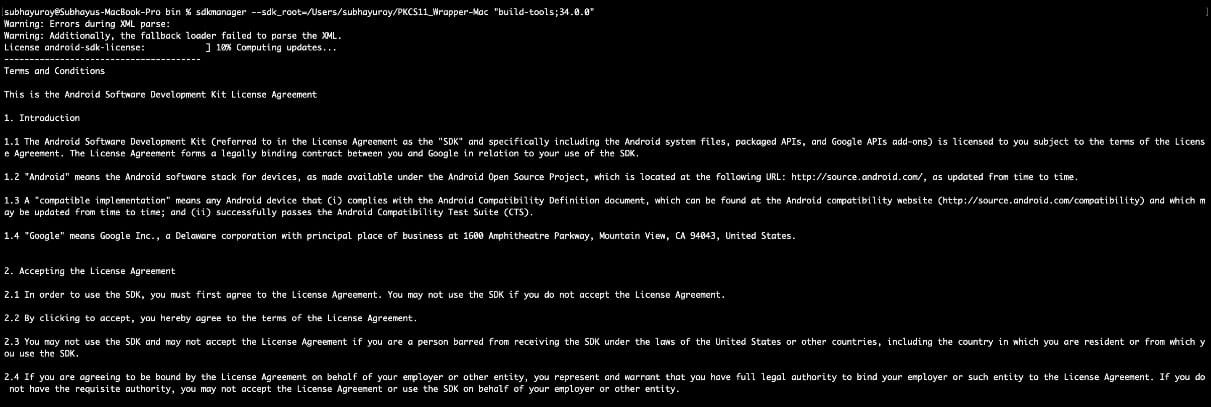
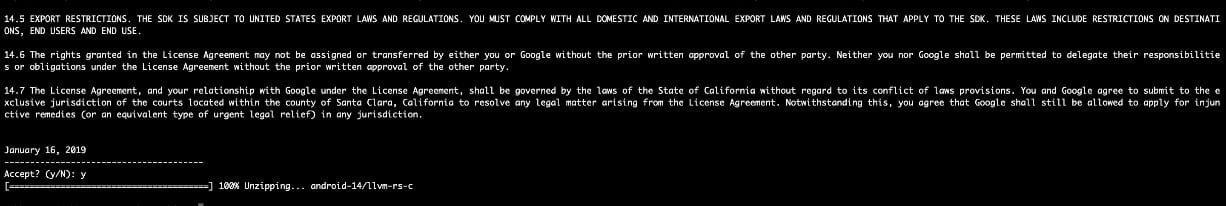
Step 5: Install Build tools using SDKManager, which contains the APKSigner: sdkmanager –sdk_root=/Users/subhayuroy/PKCS11_Wrapper-Mac “build-tools;34.0.0”
Step 6: Ensure that APKSigner is present: ls /Users/subhayuroy/PKCS11_Wrapper-Mac/build-tools/34.0.0/apksigner

Step 7: Two packages are required to run the PKCS11 Wrapper on your system. First, install liblog4cxx-dev using: brew install log4cxx
Step 8: The last prerequisite is to install the curl package: brew install curl
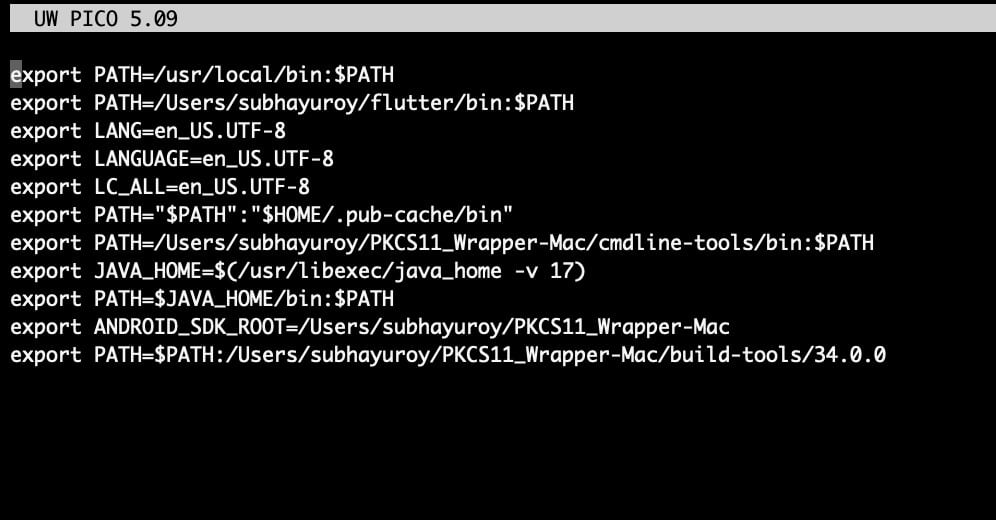
Step 9: You need to ensure all the relative paths are added to your PATH variable (~/.zshrc file):
export PATH=/Users/subhayuroy/PKCS11_Wrapper-Mac/cmdline-tools/bin:$PATH
export JAVA_HOME=$(/usr/libexec/java_home -v 17)
export PATH=$JAVA_HOME/bin:$PATH
export ANDROID_SDK_ROOT=/Users/subhayuroy/PKCS11_Wrapper-Mac
export PATH=$PATH:/Users/subhayuroy/PKCS11_Wrapper-Mac/build-tools/34.0.0
Now that all the configurations and prerequisites have been installed. Let’s perform the signing operation first.
The signing command will look something like this (ensure you run this command only inside the folder where your PKCS11 Wrapper is installed):
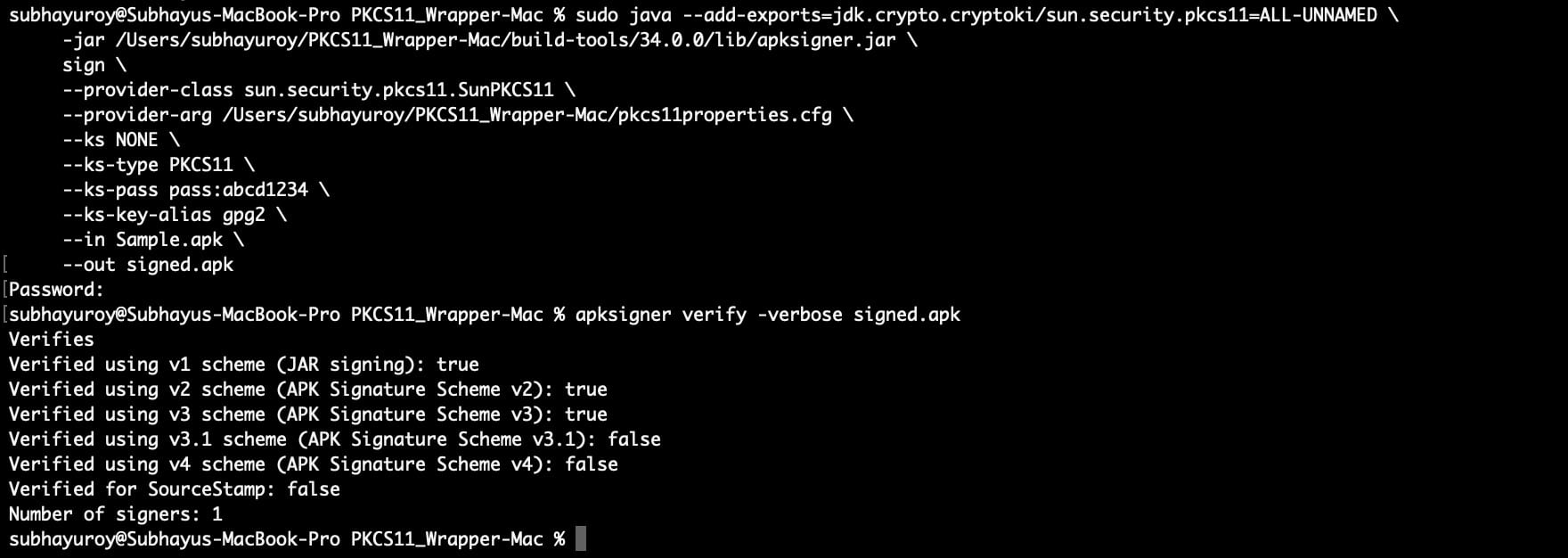
java –add-exports=jdk.crypto.cryptoki/sun.security.pkcs11=ALL-UNNAMED -jar <path of the apksigner.jar in your system> sign –provider-class sun.security.pkcs11.SunPKCS11 –provider-arg <path of the pkcs11properties.cfg file in your system> –ks NONE –ks-type PKCS11 –ks-pass pass:abcd1234 –ks-key-alias <private key alias> –in <path of the APK file you want to sign> –out <path of the Signed APK file>
For Example: java –add-exports=jdk.crypto.cryptoki/sun.security.pkcs11=ALL-UNNAMED \ -jar /Users/subhayuroy/PKCS11_Wrapper-Mac/build-tools/34.0.0/lib/apksigner.jar \ sign \ –provider-class sun.security.pkcs11.SunPKCS11 \ –provider-arg /Users/subhayuroy/PKCS11_Wrapper-Mac/pkcs11properties.cfg \ –ks NONE \ –ks-type PKCS11 \ –ks-pass pass:abcd1234 \ –ks-key-alias gpg2 \ –in Sample.apk \ –out signed.apk

After successfully signing the APK, let’s verify it using this command:
apksigner verify -verbose <path of the signed APK file>
For example: apksigner verify -verbose signed.apk
Our PKCS#11 Wrapper offers unmatched performance, including client-side hashing for faster performance and smooth integration into your existing workflows. Using our code signing solution – CodeSign Secure v3.01, you can trust end users and securely secure your apps.
By working with Encryption Consulting, you are investing in a solution that is trusted by developers and organizations worldwide to protect their software supply chain rather than just picking a tool. This is your opportunity to use our code signing technologies to advance your APK signing.
Visit our official website or get in touch with our support staff for more details or help.

March 12, 2025

February 24, 2025