Code signing is a security mechanism used to verify the authenticity and integrity of digital code. It involves adding a digital signature to code, which allows users to determine who created it and whether it has been tampered with. Code signing is commonly used to sign executable files, libraries, and scripts, but it can also be used to sign Excel Macro files.
What is Code Signing?
Code signing is a security practice that involves digitally signing software with a certificate to verify its authenticity and integrity. Code signing certificates are issued by trusted certificate authorities (CA) and allow end-users to verify that the software they are downloading or running has not been tampered with or modified since it was signed by the software publisher.
This helps to prevent malware and other malicious software from being distributed and installed on users’ systems. To establish trust in a digital signature and ensure the code has not been tampered with, popular code signing tools such as Microsoft Authenticode and Java Code Signing usually necessitate a trusted third-party certificate authority-issued digital certificate.
Signing Excel Files
Excel Macro files are used to automate tasks in Microsoft Excel. They can contain macros, which are small programs that automate repetitive tasks, such as formatting data or generating reports. Macro files can be created using the VBA (Visual Basic for Applications) programming language and can be saved with the .xlsm file extension.
Threats posed by Macros
While Office Macros remain the best option for business-critical processes, they also pose a great security threat. Macros run within Office documents with the same rights as the person who opened it. Not to mention macros that increase their privileges even further by utilizing further exploits, making Macros a powerful tool for hackers to infiltrate an organization.
But what makes Macro so dreadful? In contrast to other programs, people tend to use Office documents without hesitation. Then, it only takes a click to enable macro execution, which is particularly simple to accomplish using social engineering by embedding instructions in an email or even the document itself.
Administrators find themselves in a pinch when it comes to Macros mainly because of these reasons:
- It is almost impossible to provide policy settings that can define which macros may be executed.
- Policy frameworks such as application control/whitelisting do not work for macros.
- Some malicious macros can bypass malware detectors.
Now the question arises, what can be done to secure ourselves from Macro threats? The answer is simple, implement Macro Signing to create secure End User Policies.
By signing an Excel Macro file, you can ensure that users can trust the code in the file and that it has not been tampered with. Digitally signing your organization’s macros creates the foundation for Policy capabilities of MS Office. This empowers you to
- Use group policies to allow execution only for macros signed with trusted certificates, and
- Assign trusted certificates to users and groups.
Using CodeSign Secure, we can make the signing and verifying process simple. Our process involves client-side hashing to increase server speed and using HSMs to store private keys, ensuring a low attack surface and speedy, secure signing of files.
Limitations in Current Approaches
This table highlights how easily accessible policies either have insufficient security or have an unacceptably negative impact on the business:
| Method | Security level | Implementation | Business Impact | Remarks |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Let users decide whether to Enable the execution of macros | Medium | High | High | You can’t always rely on users to make the best choices |
| Enable macro execution | Low | High | High | It is never appropriate to enable this. |
| Disable macro execution except for digitally signed macros | Medium-high | Medium | High | The process of digital signing in Office is laborious and necessitates macro writers having access to their development PCs’ private keys. |
| Disable macro execution except for users who require them | Medium-high | Low | Medium | Each of these users is still dangerous, and their numbers frequently increase. |
| Disable macro execution except for certain storage locations | Medium-high | Medium-high | Medium-high | Although direct online and email attacks will be lessened as a result, anyone can still leave a harmful document in a reliable place. |
| Disable macro execution for everyone | High | High | Low | Very safe but often unrealistic |
| Using CodeSign Secure- Disable macro execution except for digitally signed macros | High | High | High | Provide a more secure procedure that complies with macro execution policies for signing authorization and approval policies. |
Step-by-step Signing Process
Here are the steps to sign an Excel Macro file. First, we must install the required tools
Step 1
We must install Windows SDK, which provides libraries and tools for building Windows apps. This development kit will install a tool called signtool, which is included as a part of the Windows SDK. Click Download the Installer and run it once it is done downloading.
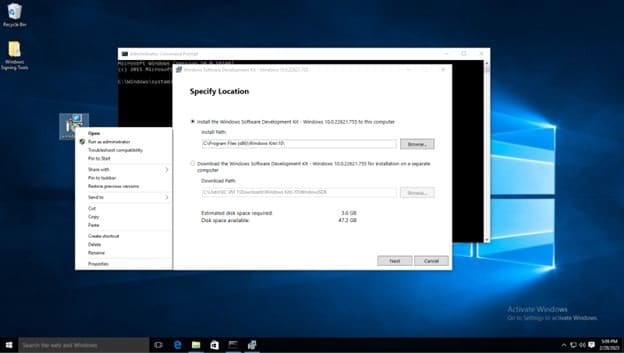
You can choose to install only the Windows SDK Signing Tools for Desktop Apps.
Note: Remember the default path shown in the install path, as this will be helpful with running these commands from the command prompt.
On the Windows Kits Privacy page, either option for allowing Microsoft to collect insights is okay. Click next.
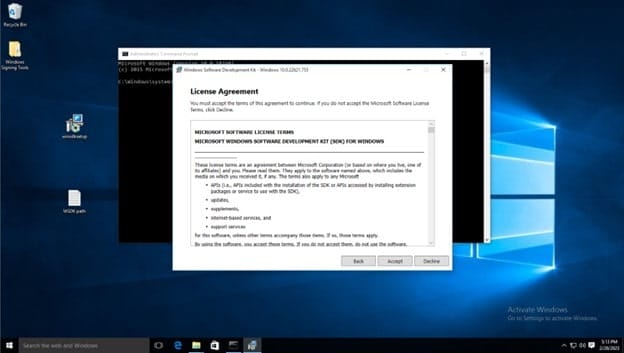
Accept the License agreement

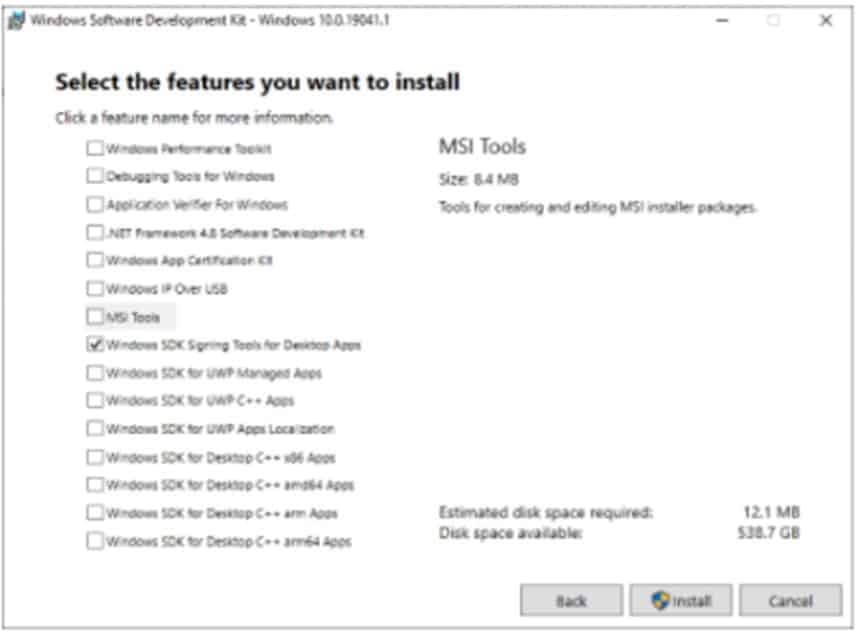
Deselect every feature except for Windows SDK Signing Tools for Desktop Apps, then select install. We don’t need every feature for the signing process to work.
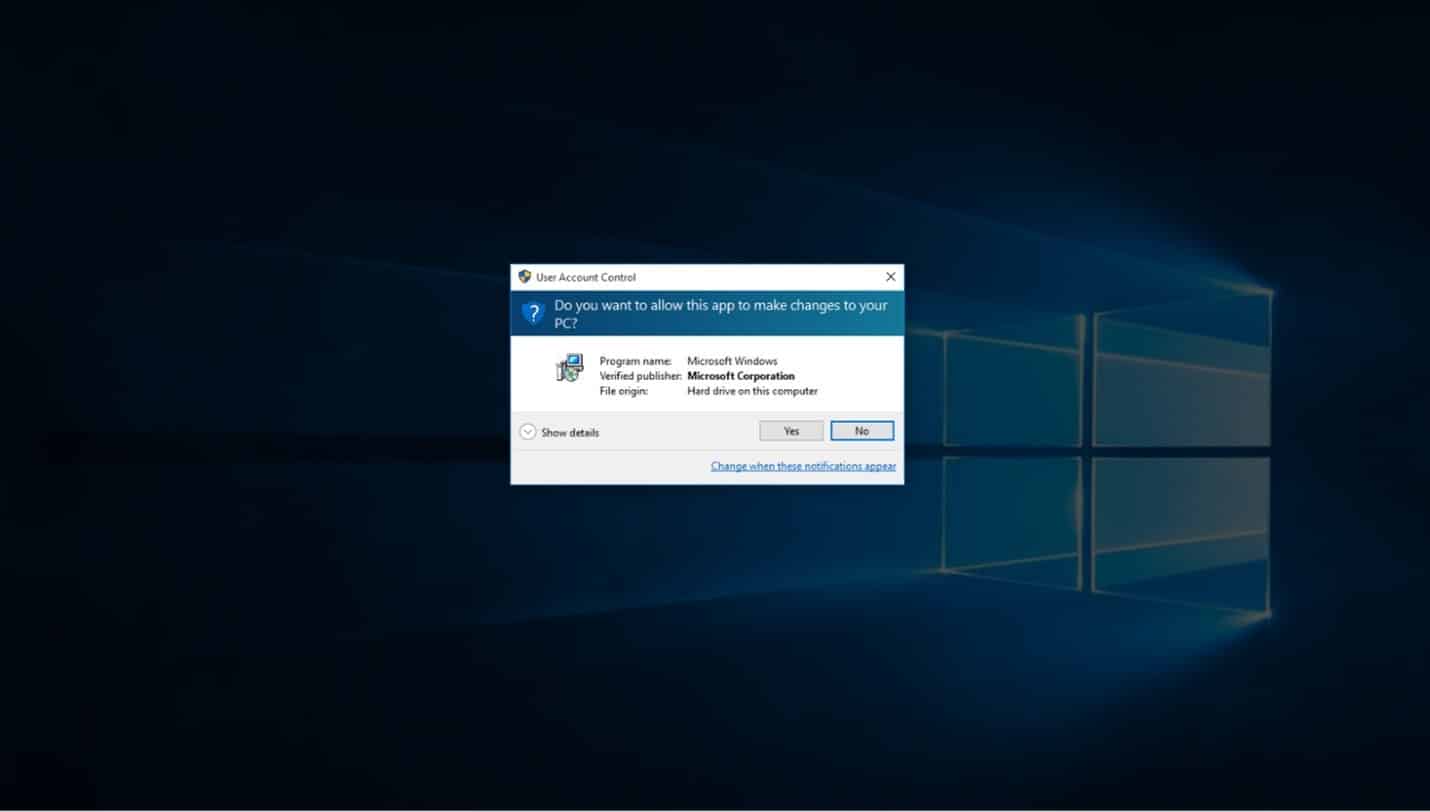
When prompted if you want to allow this app to make changes, select yes.
Lastly, select close, and next we have to add a path to the system environment variables in order to run commands from the Command Prompt effectively.
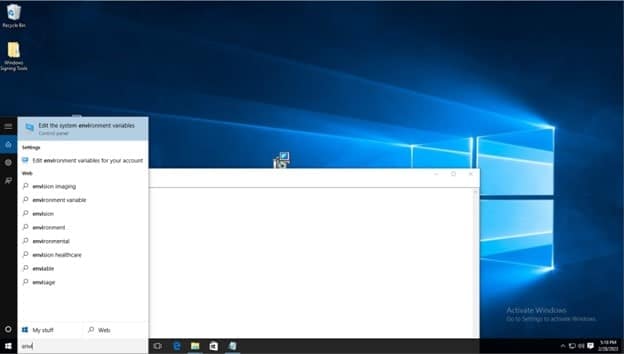
Click on windows search bar on task bar and type “Edit the system environment variables” and select the control panel option of the same name.
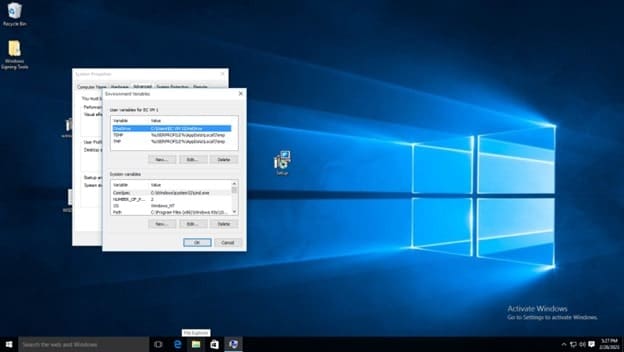
Click environment variables
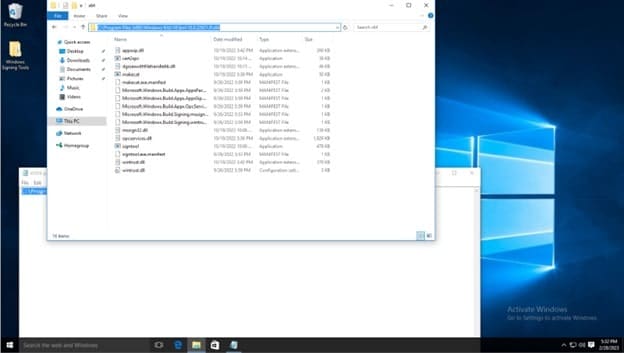
Before editing the variable list, navigate to where the Windows SDK is installed to using file explorer, you must copy the path of the folder which contains the signtool application, the default path is C:\Program Files (x86)\Windows Kits\10\bin\10.0.22621.0\x64, refer to the below screenshot. Make sure to right click and copy the path as shown. You can also see the signtool application at the bottom of the file list, this is the command you will run.
In the System Variables list, click new. Then type Path as the variable name, and copy and paste the aforementioned path. Then click OK on the environment variables window and system properties window.
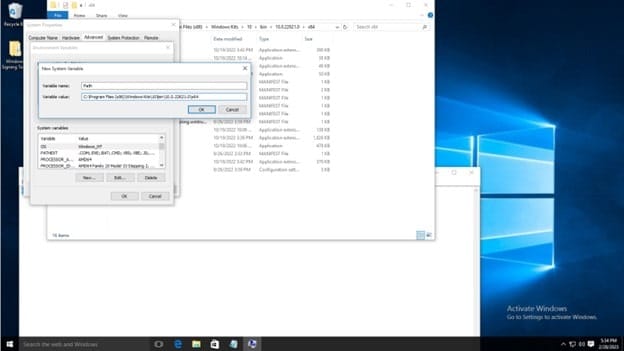
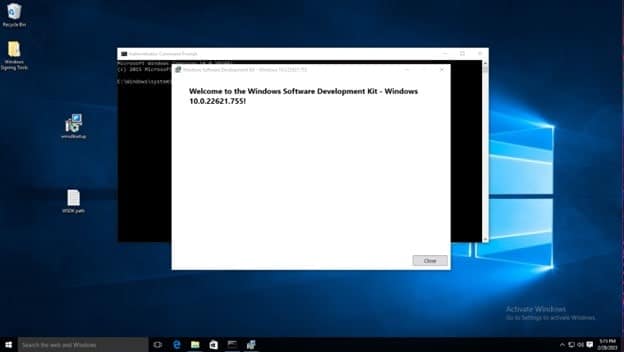
To test the installation, open the command prompt, and type signtool, and the output should be as shown below.

The default signtool installation location is, for example: C:\Program Files (x86)\Windows Kits\10\bin\10.0.22621.0\x64
Step 2
Download and install the Subject Interface Package for Digitally Signing Microsoft Office Files
This link goes to Microsoft’s download page for an Interface Package. This download includes two Subject Interface Package (SIP) libraries that support the digital signing and signature verification of Visual Basic for Applications projects within most Office file formats that support VBA macros. These are required to make signtool recognize .xls and .xlsm files. After downloading the installer, follow the steps below.
After the .exe is downloaded, open it, and choose an installation folder, or create a new folder as shown below:
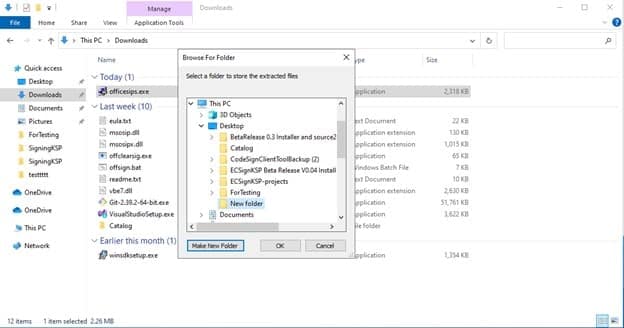
It will say that the files were extracted successfully, and you’ll find your installation folder populated with some files. These are the libraries that will are essential to enabling signing Excel Macros. We must run a pair of commands to install these .dll files into the registry.
Open an administrator command prompt and type the following, the path will be where you just installed the files:
regsvr32.exe <complete path to msosip.dll>
regsvr32.exe <complete path to msosipx.dll>
For more information on how to register OLE controls, visit Microsoft’s website.
If successful, you will see a message: “DIIRegister Server in <complete file path> succeeded.”
Step 3
Then we must download the Microsoft Visual C++ Redistributable Installer. These libraries are required by many applications built by using Microsoft C and C++ tools. Since the tools we’re using require these libraries, it is necessary to install them. For more information, see Microsoft’s documentation.
Microsoft Visual C++ Redistributable Installer Download Link:
Run the installer, accept the terms and conditions, and click install.
Step 4
Now we can use the command prompt to sign our files. Signing Windows Excel Macro files is possible using the signtool command. The /kc is going to be the name of your certificate, /f is going to be the path to the certificate.pem file, /fd and /td are the desired algorithms, /csp is the name of the crypto storage provider (in this case Encryption Consulting Key Storage Provider), /tr is the address of the timestamp server, then after the /td SHA256 is the path in quotations of the file to be signed.
With this case of macro signing, you can use .xls or .xlsm file extensions and run the signing command.
signtool sign /csp “Encryption Consulting Key Storage Provider” /kc evcodesigning /f C:\Users\Administrator\Desktop\ForTesting\evcodesigning.pem /fd SHA256 /tr http://timestamp.digicert.com /td SHA256 “C:\Users\Administrator\Desktop\ForTesting\MacroTest.xlm”

Step 5
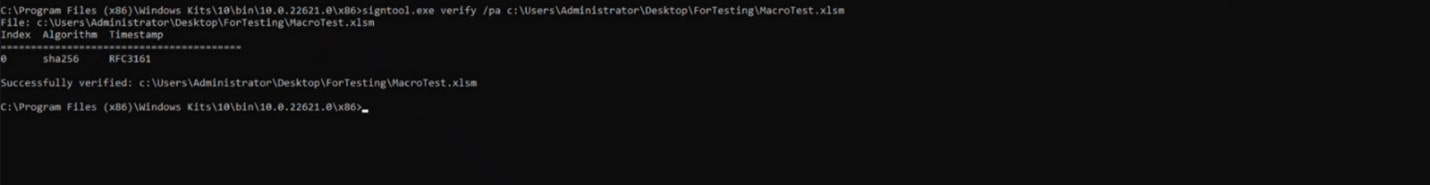
After signing the file, you can verify the file and list information about it. To verify the signed file, simply use the verify command:
signtool.exe verify /pa C:\Users\Administrator\Desktop\ForTesting\MacroTest.xlsm
Conclusion
Once the Excel Macro file is signed, users who open the file will see a warning message that the file contains macros, but they will also see the digital signature and can verify that it is valid. If the digital signature is not valid, users will be warned that the file may contain malicious code and may be unsafe to open.
To summarize, incorporating code signing into software security is crucial to safeguard it against malware attacks and tampering. Encryption Consulting’s Code Sign Secure offers various advantages, including seamless integration with development workflows, robust authentication and encryption, and customizable pricing options. To learn more about how you could use Code Sign Secure visit: Code Sign Solution or contact us at: info@encryptionconsulting.com




