Certificate Enrollment is the process by which an entity, such as an individual or an organization, requests and obtains a digital certificate from a Certificate Authority (CA). Digital certificates are used to secure communications and authenticate the identity of a server, client, or user in various secure protocols like SSL/TLS (for securing websites), S/MIME (for email encryption and signing), and more.
The primary purpose of certificate enrollment is to obtain a digital certificate that contains a public key and associated identity information (such as the Common Name, Organization, etc.). The CA signs the certificate, establishing a trusted relationship between the public key and the entity’s identity. This process ensures that the entity’s identity is validated and that the public key can be used securely for encryption, digital signing, or other cryptographic operations.
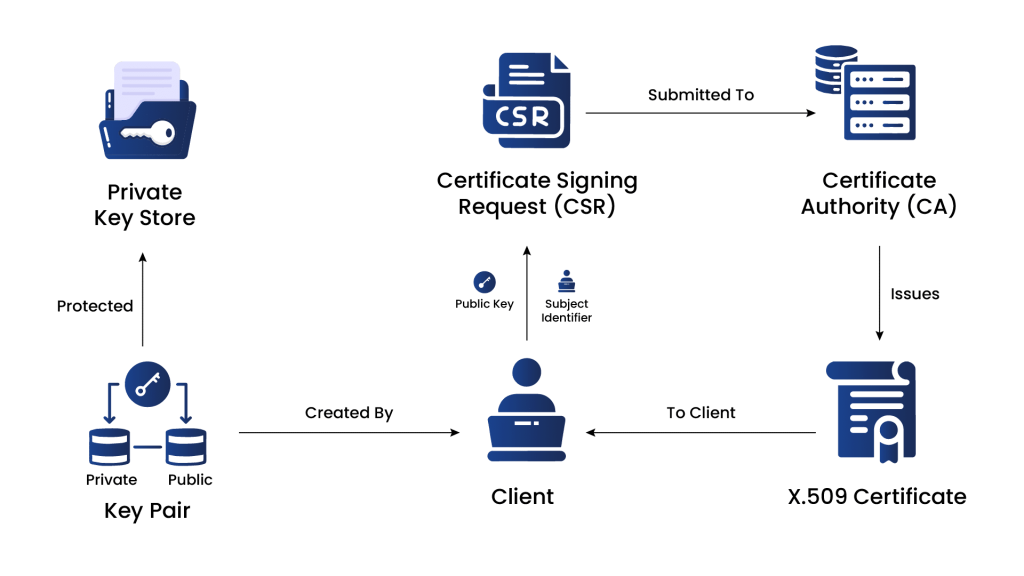
The Comprehensive Lifecycle of Certificate Enrollment
-
Certificate Signing Request (CSR)
To initiate the certificate enrollment process, the entity generates a Certificate Signing Request (CSR). The CSR includes the public key and information about the entity that needs to be included in the certificate, such as the domain name for SSL/TLS certificates or the email address for S/MIME certificates.
-
Submitting the CSR to the CA
The CSR is submitted to the CA during the enrollment process. The CA verifies the identity of the entity and the information in the CSR. The CA may use various methods to verify the entity’s identity, such as email verification, domain validation, or manual verification of legal documents.
-
Certificate Issuance
Once the CA has completed the verification process and is satisfied that the entity is legitimate, it issues a digital certificate. The certificate contains the entity’s public key, identity information, validity period, and the CA’s digital signature.
-
Certificate Delivery
The issued certificate is delivered back to the entity. Depending on the CA and the certificate type, the delivery may be done through email, a secure portal, or other methods.
-
Certificate Installation
The entity needs to install the issued certificate on the appropriate server or device where it will be used. For example, in SSL/TLS, the certificate is installed on the webserver to secure the website’s connections.
-
Certificate Use
Once installed, the certificate is ready for secure communication protocols. Clients, users, or other entities interacting with the certificate holder can verify the certificate’s authenticity through the CA’s digital signature, ensuring a secure and trustworthy connection.
-
Certificate Renewal
Certificates have a limited validity period (typically 1-2 years). Before expiration, the entity must renew the certificate through a similar enrollment process to continue using it without disruption.
Methods for Certificate Enrollment
There are several methods of certificate enrollment, each catering to different use cases and environments. These methods facilitate obtaining digital certificates from CAs for securing communications and verifying the identity of entities. Here are some common methods of certificate enrollment:
-
Manual Enrollment
Manual enrollment is a traditional method where the entity generates a Certificate Signing Request (CSR) using software or tools provided by the server or device where the certificate will be installed. The entity then manually submits the CSR to the CA for validation and issuance. This method is commonly used for obtaining SSL/TLS certificates for web servers.
-
Automatic Enrollment
Automatic enrollment, also known as auto-enrollment or certificate auto-enrollment, streamlines the certificate issuance process by automating various steps. It is particularly beneficial in large-scale environments with multiple devices or users. There are several automatic enrollment methods.
-
Active Directory Certificate Services (ADCS)
In Microsoft Windows environments, AD CS provides an auto-enrollment feature called “Certificate Services Client – Auto-Enrollment.” It allows devices and users within the Active Directory domain to request and receive certificates automatically based on predefined certificate templates and Group Policy settings.
-
Simple Certificate Enrollment Protocol (SCEP)
SCEP is a protocol commonly used in network device environments, such as routers, switches, and firewalls. It enables these devices to request and obtain digital certificates from a CA automatically. SCEP simplifies certificate enrollment for devices that may not have a traditional user interface.
-
Mobile Device Management (MDM) Enrollment
In the context of mobile devices, MDM solutions often include built-in features for certificate enrollment. MDM platforms can facilitate the enrollment process for securing mobile communication, email, and VPN connections.
-
Online Certificate Enrollment Protocol (OCEP)
OCEP is an internet draft that outlines a standard protocol for certificate enrollment using HTTP-based communication. OCEP simplifies certificate enrollment and promotes interoperability between CAs and enrollment clients.
-
Public Key Infrastructure using X.509 (PKIX)
PKIX is a widely adopted standard that defines the framework for managing digital certificates and their related components. It includes standards for certificate enrollment, revocation, and validation processes. X.509 is the format used for encoding certificates.
Certificate Enrollment Protocols
Certificate enrollment involves using various protocols to facilitate the secure exchange of certificate-related information between the entity requesting the certificate and the Certificate Authority (CA) issuing the certificate. These protocols ensure the enrollment process’s confidentiality, integrity, and authenticity. Here are some common protocols used for certificate enrollment:
-
SCEP
SCEP, stands for Simple Certificate Enrollment Protocol, is an open-source certificate management protocol facilitating easier, scalable, and secure certificate issuance.
- It operates on a request/response model using HTTP and supports RSA-based cryptography.
- The certificate signing request (CSR) must include a ‘challenge password’ shared between the server and the requester, enhancing authentication.
- SCEP does not support online certificate revocation and has limited Certificate Revocation List (CRL) retrieval support.
1.1 Workflow of SCEP Protocol
- Obtain and validate a copy of the CA certificate.
- Generate CSR and send it to CA.
- Poll the SCEP server to verify whether the certificate is signed.
- Re-enroll to obtain new certificates before the existing certificate expires.
- The preferred method is via a CRL distribution point (CDP) query.
- Retrieve the CRL as needed.
The SCEP enrollment and usage generally follow this workflow:
1.2 Understanding the Benefits of the SCEP Protocol
- Getting certificates for public key infrastructure involves exchanging information and approvals with a trusted certification authority service.
- SCEP automates this process, making it easier and faster for IT security teams to get and install device certificates without manual work.
- Devices can easily enroll for certificates using a URL and a shared secret to communicate with the certification authority service.
- Mobile Device Management systems like Microsoft Intune and Apple use SCEP to get certificates for smartphones and other mobile devices quickly.
-
Enrollment Over Secure Transport (EST)
Enrollment over Secure Transport (EST) is a certificate management protocol that automates issuing and provisioning X.509 certificates.
- EST is defined in RFC 7030 and is designed for clients using public key infrastructure (PKI), such as web servers, applications, and endpoint devices.
- The protocol enables PKI clients to request certificates from trusted Certificate Authorities (CAs) and receive them securely over HTTPS without human intervention.
- EST’s main goal is to simplify and secure the certificate enrollment process, reducing the risk of misconfigurations, outages, and security compromises caused by human errors.
- Automated enrollment through EST also frees up time for PKI personnel, allowing them to focus on other essential tasks.
2.1 Workflow of EST Protocol
- EST client initiates a certificate enrollment request to the Certificate Authority (CA) over a secure HTTPS connection.
- The EST client may include additional information, such as certificate attributes and authentication credentials, in the request.
- The CA verifies the client’s identity and authorization to obtain the requested certificate.
- If approved, the CA securely issues the certificate to the EST client over the established HTTPS connection.
- The EST client receives the issued certificate and can use it for secure communication and authentication purposes.
2.2 Understanding the Benefits of EST Protocol
- EST uses TLS to transport messages and certificates.
- Secure CSR authentication in EST links the CSR to a trusted requestor and authenticates it with TLS, preventing unauthorized certificate issuance.
- EST supports advanced cryptographic algorithms such as ECC and ECDSA, enhancing cryptographic agility and efficiency.
- Automated certificate renewal is supported in EST, making the process seamless and efficient.
- EST allows server-side key generation, which benefits resource-constrained environments and devices.
- EST lacks a built-in mechanism for retrieving certificate revocation status but can utilize options like OCSP and OCSP stapling.
-
Automated Certificate Management Environment (ACME)
ACME (Automated Certificate Management Environment) is a communications protocol.
- It automates CSR generation and certificate/key rotation.
- Primarily used by Let’s Encrypt for issuing 90-day Domain Validated certificates and automating renewals.
- Developed by the Internet Security Research Group (ISRG) for Let’s Encrypt and offered as an open-source tool.
- Being adopted by other CAs, PKI vendors, and browsers to support various certificate types like S/MIME and Code-signing.
- Requires CA to access the DNS/HTTPS token for implementation.
- Suited for internal PKI issuance method.
3.1 Workflow of ACME Protocol
- The ACME client registers with the Certificate Authority (CA).
- The client proves domain ownership through challenges (HTTP-based or DNS-based).
- The client creates an order for the desired certificate.
- The CA presents challenges to confirm domain ownership.
- After completing challenges, the CA issues the certificate to the client.
- The client installs the issued certificate on the server or device.
- The client can initiate renewal as the certificate’s validity nears expiration.
- The client can initiate certificate revocation if needed.
3.2 Understanding the Benefits of ACME Protocol
- Eliminates potential configuration errors, leading to error-free certificate management and reduced downtime.
- Enhances security by supporting low-validity DV certificates, improving certificate rotation and overall security posture.
- Enables quick CA and key migration, allowing users to swiftly switch to a different CA in case of a compromise.
- Improves ecosystem quality by providing a uniform protocol for developers, simplifying integration, and promoting consistency.
- Saves time, effort, and costs through automated certificate processes.
- ACME is an open-source protocol freely available for use.
Comparison of Certificate Enrollment Protocol
| Category | EST | SCEP | ACME |
|---|---|---|---|
| Purpose | EST is used for secure certificate enrollment and management. | SCEP serves the same purpose with a focus on client certificates. | ACME automates certificate provisioning and renewal for web servers. |
| Certificate Type | Supports X.509 certificates. | Supports X.509 certificates. | Supports X.509 certificates. |
| Authentication | EST employs mutual authentication between the client and the CA server. | SCEP relies on client certificate-based authentication with the CA server. | ACME uses domain-based authentication with its server. |
| Standardization | EST is standardized in IETF RFC 7030. | SCEP lacks a specific standard but is an industry practice. | ACME follows IETF RFC 8555. |
| Certificate Rotation | EST supports automated certificate renewal and rotation. | SCEP typically requires manual renewal with limited rotation. | ACME automates both the renewal and rotation of certificates. |
| Security | EST offers strong security with mutual authentication and encryption. | SCEP is generally secure but may lack some modern security features. | ACME provides strong security with domain-based authentication and automated certificate renewal. |
Conclusion
Certificate enrollment is vital for obtaining digital certificates from Certificate Authorities (CAs) to secure communication and authentication. The comprehensive lifecycle of certificate enrollment includes generating a Certificate Signing Request (CSR), submitting it to the CA, certificate issuance, delivery, installation, and renewal.
Different certificate enrollment methods, such as manual and automatic enrollment, cater to diverse use cases and streamline the process while reducing errors. Certificate enrollment protocols like SCEP, EST, and ACME enhance security and efficiency. SCEP simplifies enrollment in network devices, EST supports advanced cryptographic algorithms and automated renewal, and ACME automates CSR generation and certificate rotation. By leveraging automated enrollment processes and standardized protocols, organizations can ensure a seamless, secure, and efficient certificate issuance process, bolstering overall security.
How can Encryption Consulting help?
Encryption Consulting provides a specialized Certificate Lifecycle management solution CertSecure Manager. From discovery and inventory to issuance, deployment, renewal, revocation, and reporting. CertSecure provides an all-encompassing solution. Intelligent report generation, alerting, automation, automatic deployment onto servers, and certificate enrollment add layers of sophistication, making it a versatile and intelligent asset.

