- Let’s Understand the ACME Protocol
- How CertSecure Manager Redefines ACME Integration
- Transforming ACME Limitations into Strengths
- Best Practices for Certificate Management
- Real-World Use Case of CertSecure Manager with ACME
- Driving Innovation with CertSecure Manager
- Why CertSecure Manager Stands Out
- Conclusion
Scalability and automation are critical for modern enterprises, especially in certificate management. With cyber threats evolving and computational advancements highlighting the need to secure digital assets, certificate management has become a cornerstone of cybersecurity strategy. The shift toward shorter certificate validity periods, such as Google’s proposal for 90-day certificates, exposes the inefficiencies of manual processes. According to the 2023 State of Machine Identity Report, 77% of organizations faced at least two certificate-related outages in the past two years due to expired certificates. Untracked or “shadow” certificates can cost millions annually due to unplanned expirations (GlobalSign), underscoring the need for robust automation.
The ACME Protocol (Automated Certificate Management Environment) addresses this by automating certificate issuance and renewal, reducing human error and administrative overhead. However, CertSecure Manager by Encryption Consulting elevates ACME’s capabilities, offering an enterprise-grade solution tailored for modern organizations. With features like compliance enforcement, real-time monitoring, and seamless integration, CertSecure Manager ensures automated, secure, and reliable certificate management.
In this blog, we’ll explore how CertSecure Manager’s ACME integration helps your organization achieve seamless certificate lifecycle management (CLM).
Let’s Understand the ACME Protocol
The ACME protocol, created by the Internet Security Research Group (ISRG) and popularized by Let’s Encrypt, is an open standard defined in RFC 8555. It was introduced to automate interactions between Certificate Authorities (CAs) and clients, streamlining the process of certificate issuance, validation, renewal, and revocation. The principal objective was to eliminate manual intervention and simplify the complexities of maintaining secure digital certificates for public key infrastructure (PKI), such as managing domain validations and handling multi-step certificate renewals.
Key Concepts of ACME
-
Certificate Request Initiation
The certificate issuance process begins with the ACME client initiating a CSR to the ACME server. This step forms the foundation of the ACME protocol workflow and ensures that the requester’s intent and requirements are clearly communicated to the issuing authority.
How it Works
-
Generating the Key Pair
- The ACME client generates a public-private key pair if not already available.
- The private key is securely stored by the client, while the public key forms part of the CSR.
-
Creating the CSR: The CSR includes essential details
about the certificate request, such as:
- Public Key: Used for encrypting data and verifying the identity of the certificate owner.
- Subject Information: Contains the fully qualified domain names (FQDNs) for which the certificate is requested (e.g., example.com).
- Optional Attributes: This may include organization details if the certificate type supports it.
-
Sending the Request
- The CSR is transmitted to the ACME server using a secure HTTPS connection.
- The ACME client signs the CSR with its account key to ensure authenticity and integrity.
Considerations
- Validation-Ready CSR: The CSR is structured in a way that facilitates seamless validation through ACME-supported challenges (e.g., HTTP-01, DNS-01).
- Secure Communication: The ACME protocol mandates secure connections for CSR submission, protecting the data from interception or tampering.
Key Features
- Domain Coverage: Ensure that all intended domain names are included in the CSR, especially if the certificate is for multiple domains (SAN certificate).
- Key Strength: Use strong cryptographic algorithms (e.g., RSA 2048-bit or ECC) to generate the key pair, adhering to security best practices.
- Account Key Management: The account key used to sign the CSR must be securely stored to prevent unauthorized certificate requests.
-
Generating the Key Pair
-
Domain Validation Challenges
The ACME server issues validation challenges to verify domain ownership or control. These challenges are essential to ensure that the entity requesting the certificate has legitimate control over the domain. Based on publicly available information from the ACME protocol (RFC8555, section 9.7.8) and Let’s Encrypt documentation, the ACME protocol supports several types of validation challenges:
HTTP-01 Challenge
- Overview: The ACME client places a token in a specific file on the web server to prove domain ownership.
-
How it works:
- The ACME client receives a token and a URL path from the ACME server.
- The client creates a file containing the token and places it at the specified URL path on the web server.
- The ACME server makes an HTTP request to the URL to verify the presence of the token.
- If the token is found and matches the expected value, the domain is validated.
-
Use Case: Suitable for web servers that can easily
serve static files.
Pros Cons 1. Easy to automate without in-depth knowledge of a domain’s DNS or server configuration.
2. Works well with off-the-shelf web servers.
3. Enables hosting providers to issue certificates for domains CNAMEd to them.1. Not suitable if the ISP blocks port 80, which can be a problem for residential ISPs (though rare).
2. Cannot be used to issue wildcard certificates.
3. Manual configuration is required on multiple web servers if you have a distributed setup, ensuring the file is available on all servers. - Considerations: The HTTP-01 challenge can only be completed via port 80 (HTTP). This restriction ensures greater security and simplifies the process, though it might be an obstacle if your network or server environment has specific restrictions.
DNS-01 Challenge
- Overview: The ACME client proves domain ownership by adding a TXT record in the DNS for the domain.
-
How it works:
- The ACME server generates a token and sends it to the ACME client.
- The client creates a DNS TXT record for the domain, with the token as the value.
- The ACME server queries the DNS record to verify the presence of the token.
- If the TXT record is found and the token matches the expected value, the domain is validated.
-
Use Case: Ideal for scenarios where DNS records can be
easily updated, such as when using DNS providers with API support. Also,
it is best for scenarios requiring wildcard certificates or when a web
server is not used for validation.
Pros Cons 1. Can be used to issue wildcard certificates, unlike the HTTP-01 challenge.
2. Works well in environments with multiple web servers.
3. Ideal if you cannot open port 80, as it relies on DNS rather than HTTP.1. It requires DNS provider API access to automate the creation of DNS records, which might not be available with all DNS providers.
2. Storing DNS API credentials on your server can be a security risk, so it’s recommended to use narrowly scoped API keys or manage them from a separate, secure server. - Considerations: DNS propagation times can vary between DNS providers, potentially causing delays in validation. Some providers offer APIs to check DNS propagation status, which can help streamline this process.
TLS-SNI-01 (Deprecated)
- Overview: This challenge used a TLS handshake to validate domain control, but it has been deprecated due to security issues.
-
How it works:
- The ACME server initiated a TLS handshake on port 443 with a special Server Name Indication (SNI) header.
- The token was placed in the server’s certificate associated with that SNI.
- If the correct certificate was presented during the handshake, domain validation was successful.
- Considerations: The TLS-SNI-01 challenge was part of the initial ACME standard but has since been deprecated due to security concerns. It worked by performing a TLS handshake on port 443 (HTTPS) and looking for a specific Server Name Indication (SNI) header that contained the validation token. The TLS-SNI-01 challenge was disabled in March 2019, as it was deemed insufficiently secure.
TLS-ALPN-01 Challenge
- Overview: The ACME server provides a token that the client must present during a TLS handshake using the ALPN (Application-Layer Protocol Negotiation) extension.
-
How it works:
- The ACME client receives a token from the ACME server.
- The client configures the web server to respond to a specific TLS request with the token using the ALPN extension.
- The ACME server initiates a TLS handshake with the web server and checks for the presence of the token.
- If the token is presented correctly, the domain is validated.
-
Use Case: Suitable for environments where HTTP and DNS
challenges are not feasible, such as reverse proxies or TLS termination
points, and the web server supports ALPN.
Pros Cons 1. Works even if port 80 is unavailable.
2. Validation occurs entirely at the TLS layer, which is useful for environments where managing HTTP is difficult.
3. Avoids the need for HTTP-based validation while ensuring secure certificate issuance1. Not widely supported by popular web servers like Apache or Nginx now. Only a few tools and servers, like Caddy, currently support it.
2. Like the HTTP-01 challenge, if you have multiple servers, each must respond with the same content for validation to pass.
3. Cannot be used for wildcard domains. - Considerations: Ideal for large hosting providers or reverse proxies that need to perform host-based validation purely over TLS.
-
Authorization and Certificate Issuance
Once the validation challenges are completed successfully, the ACME protocol proceeds with domain authorization and certificate issuance. This ensures that certificates are issued only to entities with legitimate control over the domain.
How it Works
-
Domain Authorization:
- After the ACME client successfully completes the validation challenge, the ACME server verifies that the entity requesting the certificate has met the necessary criteria for domain control.
- The server updates its records to authorize the domain for certificate issuance.
-
Certificate Issuance:
- The ACME client submits a Certificate Signing Request (CSR) to the ACME server, which includes the public key and desired domain names.
- The ACME server evaluates the CSR against the validated domains and confirms compliance with its policies.
- If approved, the ACME server issues the requested certificate in the desired format (e.g., PEM or CER).
Key Security Features
- Trust Validation: The process ensures that only entities that have proven domain control can obtain certificates, reducing risks of certificate mis-issuance.
Considerations
- Certificates issued by the ACME server are often short-lived (e.g., 90 days for Let’s Encrypt), emphasizing the need for efficient renewal processes.
- Organizations must ensure secure storage of private keys used in the CSR to avoid potential compromises.
Benefits
- The Security Authorizations involved in the ACME workflow drastically minimize the risk of domain impersonation or fraud.
- Overall, ACME streamlines and simplifies the certificate issuance process by automating the validation-to-issuance workflow.
-
Domain Authorization:
-
Automated Certificate Renewals
ACME protocol mandates that certificates are automatically renewed before expiry, mitigating risks of outages or lapses in security. Manual renewals can take up to 2 hours per server (CPO Magazine), while automation ensures continuity. Thus, automation is crucial for maintaining continuous security without manual intervention. While automation reduces manual effort, organizations need to monitor logs or alerts to ensure renewals occur as expected. Additionally, each renewal may involve generating a new private key, emphasizing the need for secure key handling practices.
While ACME provides a strong foundation for automated certificate management, it has its own limitations when used in isolation. Natively, ACME lacks advanced features such as centralized management, detailed reporting, compliance tracking, and seamless integration with existing IT infrastructure. These limitations can pose challenges for organizations that require a more comprehensive and scalable solution. Therefore, to utilize and enhance the capabilities of ACME, there must be a proper CLM solution that integrates with the ACME workflow. That is where CertSecure Manager comes into play.
How CertSecure Manager Redefines ACME Integration
At Encryption Consulting, we’ve amplified the power of ACME with the robust capabilities of CertSecure Manager. As a CLM solution, it goes beyond just a standard implementation, offering a seamless and comprehensive certificate management experience.
Strengths of CertSecure Manager’s ACME Workflow
- Scalability and Flexibility: From single domains to complex multi-application infrastructures, CertSecure Manager scales effortlessly, ensuring organizations of all sizes can achieve efficient certificate management.
- Comprehensive CA Support: CertSecure Manager integrates seamlessly with both public CAs, such as DigiCert and Entrust, and private CAs, including Microsoft PKI and EJBCA, providing organizations with diverse options.
- Customizable Certificate Templates: Our platform allows organizations to define and enforce specific requirements, ensuring compliance with industry standards and internal policies.
- Enhanced Security: By leveraging the ACME protocol’s cryptographic validation methods, CertSecure Manager ensures secure communication between the client and the CA.
- Centralized Management: CertSecure Manager provides an intuitive dashboard for monitoring, renewing, and revoking certificates across environments, from IoT devices to cloud applications.
- Automation Beyond Issuance: CertSecure Manager automates not only certificate issuance but also deployment across platforms like Apache, IIS, and load balancers such as F5, reducing downtime and human error.
Transforming ACME Limitations into Strengths
Although ACME revolutionized certificate automation, out‑of‑the‑box clients like Certbot leave gaps when it comes to enterprise requirements. CertSecure Manager fills those gaps with purpose‑built enhancements, turning potential challenges into competitive advantages:
Custom Attributes for Compliance and Reporting
Ever find yourself manually tagging certificates for billing, audits, or regulatory reports? With CertSecure Manager, you define your custom fields once—billing codes, audit flags, whatever you need—and they flow through every issuance automatically. No more spreadsheets, no more late‑night reconciliation.
Legacy Infrastructure Compatibility
Your critical apps may still live on older platforms that don’t “speak” ACME. Rather than embarking on a costly rip‑and‑replace, CertSecure Manager quietly translates ACME calls into your existing CA protocols. You get full automation without touching legacy stacks.
Expanded Certificate Support
Modern security teams juggle S/MIME for secure email, code‑signing for software releases, device certificates for IoT—and each usually means a separate process. CertSecure Manager extends ACME to cover them all under one roof, giving your engineers a unified, script‑friendly interface.
Enhanced Workflow Management
Certificate sprawl isn’t just inconvenient; it’s a risk. Our interactive dashboards show you pending approvals, renewal errors, and usage trends in real time. You can enforce role‑based approvals or set automated escalations—so nothing slips through the cracks.
Flexible CA Integration
Vendor lock‑in may not make headlines—until you need to switch providers. CertSecure Manager lets you plug in any CA—public, private, or hybrid—side by side. Rebalance your issuance load, add a new root authority, or swap providers entirely, all without rewriting your automation.
Best Practices for Certificate Management
To fully leverage CertSecure Manager’s capabilities and align with industry best practices for CLM, your organization can rely on its robust automation and centralized control to enhance security and compliance (GlobalSign). The following best practices seamlessly supported by CertSecure Manager, which helps mitigate risks, prevent outages, and maintain a strong security posture.
| Best Practice | Description |
|---|---|
| Create CLM Policy | Define usage, roles, and CAs for consistency. |
| Use Centralized Platform | CertSecure Manager offers visibility and control across environments. |
| Conduct Weekly Scans | Detect shadow certificates to prevent outages. |
| Automate Processes | Use ACME and CertSecure Manager for issuance, renewal, and deployment. |
| Enable Alerts | Get real-time notifications for expirations and compliance issues. |
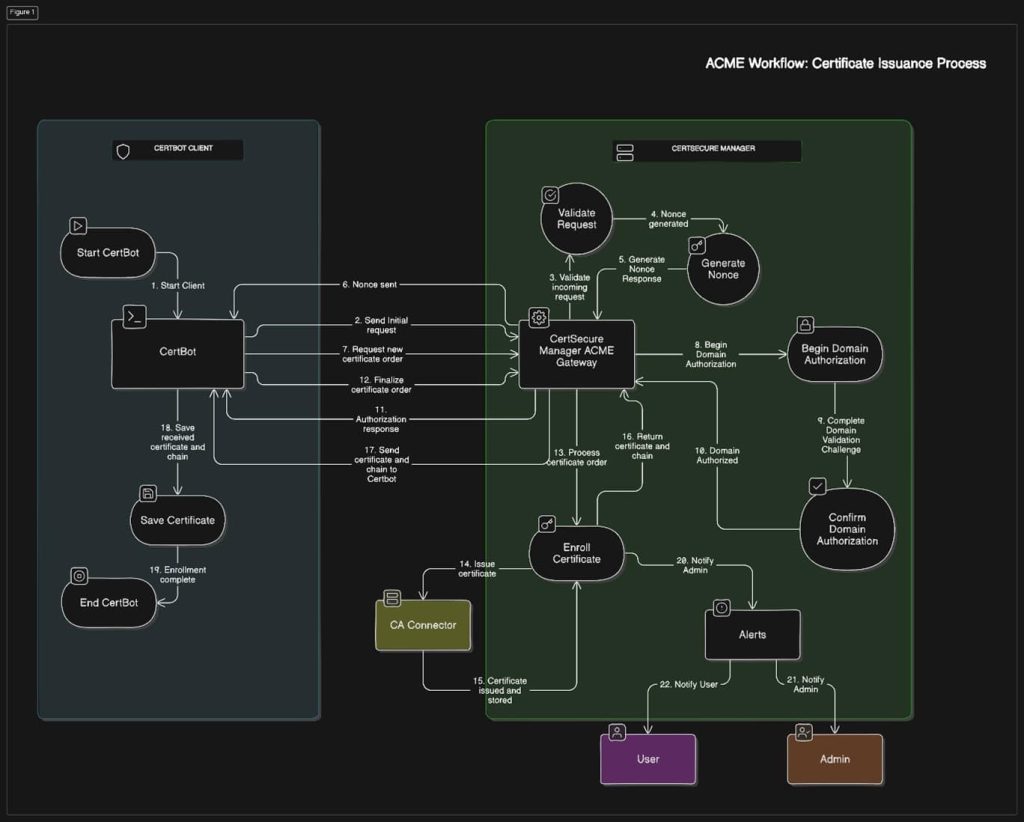
Real-World Use Case of CertSecure Manager with ACME
Let’s break down the ACME workflow with CertSecure Manager:
- Certificate Request: An ACME client, such as Certbot, initiates a request. CertSecure Manager acts as the ACME Gateway, validating the request and generating a nonce (unique token) to secure the session.
- Domain Authorization: CertSecure Manager facilitates domain validation using DNS or HTTP challenges, ensuring only authorized domain owners proceed.
- Certificate Issuance: After validation, CertSecure Manager coordinates with the CA to issue the certificate, which is securely processed and made available for deployment.
This seamless process is supported by real-time notifications and detailed reporting features, ensuring transparency and control at every step. For a comprehensive walkthrough, watch our YouTube demo showcasing CertSecure Manager’s ACME workflow in real-world scenarios.
Driving Innovation with CertSecure Manager
As industry leaders push for shorter certificate validity periods, manual processes become impractical. CertSecure Manager’s automated solutions significantly reduce the risks of expired certificates, ensuring compliance and operational continuity. By transforming ACME’s potential into real-world efficiency, CertSecure Manager empowers businesses to meet evolving demands. Below are the key advantages of CertSecure Manager, aligned with industry best practices:
Error-Free Automation for Consistent Lifecycle Management
CertSecure Manager automates the certificate renewal process, eliminating human error and reducing the operational burden of manual interventions. Industry best practices, such as those outlined in the NIST SP 800-57 guidelines for key management, emphasize automation to ensure consistent and secure cryptographic operations. By streamlining renewals, CertSecure Manager saves significant time—potentially hours per server—while maintaining accuracy across all deployments.
- Alignment with Best Practices: Automation supports the principle of least privilege and minimizes human involvement, as recommended by OWASP’s guidelines for secure certificate management. This reduces the risk of misconfigurations that could lead to outages or vulnerabilities.
- Impact: Ensures certificates are renewed on time, preventing disruptions and maintaining trust in digital infrastructure.
Robust Compliance Through Reporting and Alerts
CertSecure Manager’s comprehensive reporting and real-time alert systems ensure organizations stay compliant with regulatory and industry standards, such as PCI-DSS, GDPR, and ISO/IEC 27001. These standards mandate continuous monitoring and documentation of security controls. The platform’s actionable insights and timely notifications enable proactive adherence to security policies, simplifying audit preparation and compliance validation.
- Alignment with Best Practices: ISO/IEC 27001 emphasizes the need for ongoing monitoring and evidence of compliance. CertSecure Manager’s centralized dashboard and automated reports align with this by providing clear, auditable records of certificate status and lifecycle events.
- Impact: Reduces compliance-related overhead and ensures uninterrupted alignment with internal and external mandates.
Proactive Security with Automated Lifecycle Management
By automating the entire certificate lifecycle—from discovery to revocation—CertSecure Manager minimizes risks associated with expired, mismanaged, or compromised certificates. The CA/Browser Forum’s Baseline Requirements advocate for proactive certificate management to prevent vulnerabilities, such as those exploited in privilege escalation or man-in-the-middle attacks. CertSecure Manager’s proactive approach enhances system resilience by addressing potential threats before they materialize.
- Alignment with Best Practices: The CA/Browser Forum and NIST SP 1800-16 stress timely renewals and revocation processes to limit exposure. CertSecure Manager’s automation ensures certificates are never overlooked, supporting a zero-trust security model by maintaining valid and secure credentials.
- Impact: Strengthens organizational security posture, allowing teams to focus on strategic threat prevention rather than reactive fixes.
Why CertSecure Manager Stands Out
CertSecure Manager extends the capabilities of the ACME protocol by incorporating advanced features tailored to meet the complex requirements of enterprise environments. By addressing challenges such as short validity periods and the need for enhanced security management, CertSecure Manager ensures a seamless and secure certificate lifecycle.
- Optimized for Short Validity Periods: CertSecure Manager fully automates certificate renewals, ensuring uninterrupted operations even with certificates that expire every 90 days. This automation eliminates the risk of lapses and significantly reduces the operational overhead associated with frequent manual renewals.
- Granular Access Controls for Secure Management: The solution offers robust role-based access control (RBAC) mechanisms, enabling your organization to create tailored workflows and assign permissions based on roles and responsibilities. This ensures that only authorized personnel can access or manage sensitive certificate processes, bolstering security at every level.
- Enterprise-Grade Integration for Enhanced Security: CertSecure Manager seamlessly integrates with leading security tools like Tenable and Qualys, offering unparalleled visibility into certificate-related risks. These integrations enable proactive risk identification and mitigation, empowering your organization to maintain a strong and resilient security posture.
Conclusion
As digital security evolves, so must the tools and protocols that safeguard it. CertSecure Manager’s enhanced ACME functionality represents not just a response to industry trends but a forward-thinking approach to security and efficiency. With cutting-edge automation and compliance tools, CertSecure Manager equips businesses to stay ahead in an ever-changing landscape. To discover how CertSecure Manager can revolutionize your CLM strategy, contact us today for a personalized demo or visit our website to learn more.
- Let’s Understand the ACME Protocol
- How CertSecure Manager Redefines ACME Integration
- Transforming ACME Limitations into Strengths
- Best Practices for Certificate Management
- Real-World Use Case of CertSecure Manager with ACME
- Driving Innovation with CertSecure Manager
- Why CertSecure Manager Stands Out
- Conclusion




